Suffering from a urinary tract infection can be a painful and challenging journey. Patients commonly experience debilitating symptoms, which progresses due to a number of contributing factors. Thus, making it important for individuals to be familiar with UTI as a whole. Doing so, allows them to take initiative and seek help, especially when it’s due. At the same time, prevent the development of severe conditions due to widespread infection.
If you suspect you have a UTI, this blog will help you navigate your way towards better urinary health. Discover the basics of this condition. Let’s begin!
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)
A urinary tract infection, commonly known as a UTI, is an infection that affects any part of the urinary system. It occurs when bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), enter the urethra and travel up into the bladder or other parts of the urinary system. The urinary system consists of the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra, which can be found on the upper and lower urinary tract.
Take note that each of them is at risk of infection due to this bacteria. Here are some of the possible conditions that may happen due to widespread inflammation in the urinary system.
- cystitis – kidney infection
- pyelonephritis – bladder infection
- urethritis – urethra infection
It is important to note that this condition can occur in all genders and ages. Although, cases about UTI are more associated with women due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to reach the bladder more easily. Still, that doesn’t mean that men shouldn’t properly take care of themselves to prevent the risk of having this infection.
How Urinary Tract Infection Happen
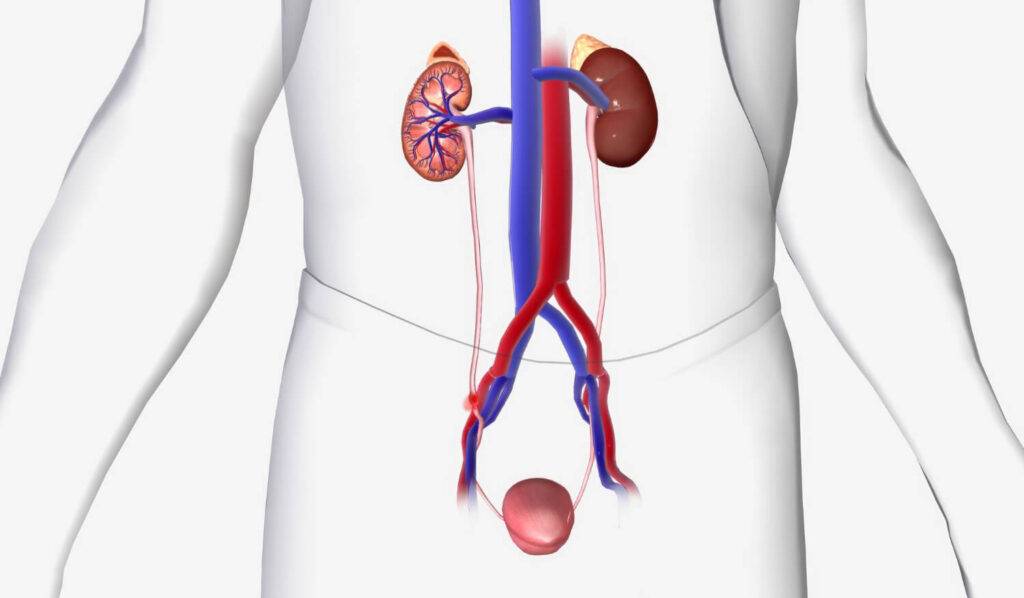
To better understand how UTI develops, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the urinary tract. The urinary system is a complex network of organs that work together to produce, store, and eliminate urine.
The kidneys, located in the upper back on either side of the spine, play a crucial role in the urinary system. They filter waste products from the blood, regulate fluid and electrolyte balance, and produce urine. Each kidney is composed of millions of tiny filtering units called nephrons, which remove waste and excess fluid from the blood to form urine.
Once urine is produced, it travels down the ureters, which are long, thin tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. The ureters use peristaltic contractions, a wave-like motion, to propel urine from the kidneys to the bladder. These contractions ensure that urine flows in one direction and prevents backflow into the kidneys.
The bladder, located in the lower abdomen, is a muscular organ that stores urine until it is ready to be expelled from the body. It expands as it fills with urine and contracts when it’s time to urinate. The bladder is lined with a protective layer of cells that help prevent bacteria from attaching to its walls.
When it’s time to urinate, the bladder sends signals to the brain, and the muscles surrounding the urethra relax, allowing urine to pass through the urethra and out of the body. The urethra, a tube that connects the bladder to the outside of the body, is shorter in women than in men, making women more susceptible to UTI.
Understanding the anatomy of the urinary tract is crucial in comprehending how UTI can occur. Bacteria can enter the urethra through various means, such as improper hygiene, sexual intercourse, or the use of catheters. Once inside, the bacteria can travel up the urinary system, causing infection and discomfort.
Causes of Urinary Tract Infections
Bacteria are the primary cause of urinary tract infections. As mentioned the most common bacteria responsible for UTI is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which is frequently found in the gastrointestinal tract. Although, there are still other contributing factors that lead to the development of this condition. Let’s discuss them below
Risk Factors for UTIs

Anatomy
While anyone can develop a urinary tract infection, certain factors increase the likelihood of experiencing one. Women are more prone to UTI due to their shorter urethra, which allows for easier anus bacteria to enter in the urethra. Thus, making it easier for bacteria to travel from the digestive tract to the urinary tract and begin bacterial growth.
Immune System
A weakened immune system can also increase the risk of developing a urinary tract infection. When the immune system is compromised, it becomes less effective at fighting off bacteria, allowing them to multiply and cause an infection. This factor also involves the other autoimmune diseases. With these conditions, the immune system will not be able to protect the patient, leading to developing diseases like UTI.
Structural Anomaly
Urinary tract abnormalities, such as structural issues or blockages, can also make it easier for bacteria to enter and infect the urinary tract. These abnormalities can be present from birth or develop later in life due to various factors. For instance, kidney stones are known for obstructing the urine flow, which can result in increased risk against a possible infection.
Catheter
Meanwhile, individuals who require urinary catheters, such as those with urinary incontinence or individuals in a hospital setting, are at a higher risk of developing urinary tract infection. The catheter provides a direct pathway for bacteria to enter the urinary tract, increasing the chances of infection. Thus, showing the importance of always changing catheters when needed.
Hormonal Changes
In terms of this last risk factor, it usually involves the normal process of aging, which means hormones dissipate. When that happens, it affects the natural protective mechanisms of the urinary tract. It is common to occur during the menopause stage as the estrogen begins to decrease.
Meanwhile, another condition that involves hormonal changes is pregnancy. However, UTI in pregnancy is influenced by other factors. Usually in this stage, the mothers can experience difficulty in relieving pee, which affects the bladder. Thus, resulting in infection.
Understanding the causes and risk factors of urinary tract infections is essential in preventing and managing these infections. By implementing proper hygiene practices, maintaining a healthy immune system, and addressing any underlying urinary tract abnormalities, individuals can reduce their risk of developing UTI.
Recognizing the Symptoms of a UTI

Recognizing the symptoms of a urinary tract infection is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. it can cause discomfort and inconvenience if not treated promptly. The sooner a UTI is identified, the quicker appropriate treatment can be initiated.
Common Symptoms
There are several common symptoms of a UTI, which can indicate the severity of the condition. Health care providers refer to these warning signs to formulate an accurate diagnosis, and provide a suitable treatment plan. That’s why it is important for patients to monitor their condition and understand the threats that UTI brings.
Here are some of the common symptoms that patients with UTI often experience:
- frequent urge to urinate
- burning sensation during urination
- cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- pelvic pain
- feeling of incomplete bladder emptying
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is essential to seek medical attention to a urology doctor promptly. UTI has the potential to worsen if left untreated and can potentially lead to complicated UTI, such as kidney infection.
When left untreated, a urinary tract infection can spread to the kidneys, causing a more serious condition known as pyelonephritis. There’s a difference in symptoms between UTI and pyelonephritis, which includes the following:
- fever
- chills
- back pain
- nausea
If you experience any of these symptoms along with the common UTI symptoms, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. There are several online platforms such as NowServing where a consultation is possible. Although, you can also visit the local hospitals near you for proximity and convenience.
Diagnosing Urinary Tract Infections
Diagnosing a urinary tract infection (UTI) can be a complex process that involves a combination of a medical history and physical examination, as well as laboratory tests to confirm the presence of bacteria. Let’s delve deeper into each step of this diagnostic journey.
Physical Examination
The urologist will proceed with a physical examination. This examination aims to identify any signs of infection or abnormalities that may be contributing to your symptoms. They may palpate your lower abdomen to check for tenderness or swelling, which can be indicative of a UTI.
In some cases, the rectum is also examined through a digital rectal examination. At the same time, be able to assess the prostate gland in men or to check for any pelvic abnormalities in women. By conducting a thorough physical examination, the healthcare provider can gather valuable clues to aid in the diagnosis of a UTI.
Laboratory Tests for UTI
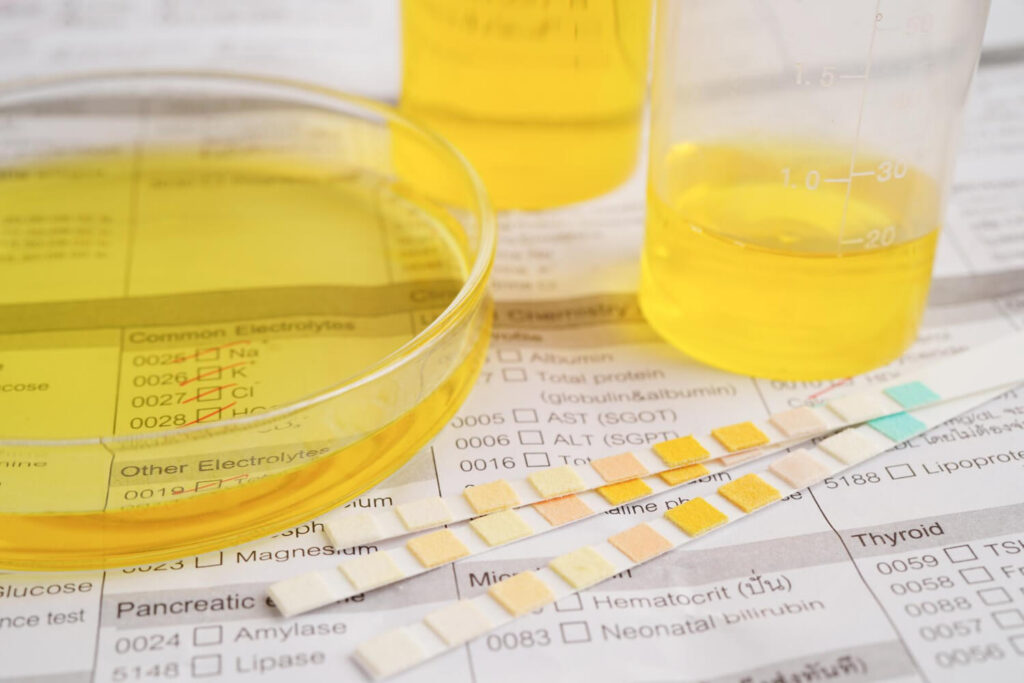
To confirm the presence of bacteria and determine the appropriate course of treatment, your healthcare provider may order laboratory tests, such as a urine culture or urinalysis. These tests play a crucial role in diagnosing UTI and guiding treatment decisions.
A urine culture involves collecting a urine sample and incubating it in a laboratory to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection. This test helps determine the most effective antibiotic for treatment. It also provides information about the bacterial load, which can help assess the severity of the infection.
On the other hand, a urinalysis involves analyzing the physical, chemical, and microscopic properties of the urine sample. It can detect the presence of white blood cells, red blood cells, and bacteria in the urine, all of which are indicative of a UTI. Additionally, a urinalysis can evaluate the pH level of the urine and the presence of any substances, such as glucose or protein, that may suggest an underlying condition contributing to the infection.
Both the urine culture and urinalysis are valuable diagnostic tools that complement each other, providing a comprehensive assessment of the infection. By analyzing the results of these tests, your healthcare provider can make an accurate diagnosis and determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific UTI.
Remember, diagnosing a UTI is a meticulous process that requires careful consideration of your medical history, a thorough physical examination, and the analysis of laboratory tests. By following this comprehensive approach, healthcare providers can ensure an accurate diagnosis and provide you with the most effective treatment to alleviate your symptoms and promote a speedy recovery.
Treatment Options and Managing UTI

Treating urinary tract infections typically involves a course of antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection and relieve symptoms. Although, some remedies can also help with the patient’s health, such as improving diet and other lifestyle choices.
Antibiotics for UTI
Your healthcare provider will prescribe a specific antibiotic based on the type of bacteria causing the infection and other variables such as your medical history and any allergies. The patient can also ask questions about the medications, especially in terms of side effects, duration, etc.
It’s crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve, to ensure the complete eradication of the infection.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to antibiotics, there are several home remedies and lifestyle changes that can help manage the symptoms of a UTI and prevent recurrent infections. These include staying hydrated, urinating regularly, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding irritating substances such as certain feminine hygiene products and perfumed soaps.
Follow up Check up
Aside from the prescribed medicine and lifestyle changes, it is also important to seek follow up check up, especially if the symptoms persist. Doing so allows to prevent recurrent UTIs and discover underlying threats. Thus, ensuring a healthier urinary health and overall well being.
Final Takeaway
Urinary tract infection is a condition that can occur without people noticing, unless the symptoms appear. That’s why it’s best to do everything to prevent UTI from developing. It can happen through understanding how UTI happens and when to seek immediate help. The basics are available to help every patient recover from this condition. It’s only a matter when and how the patient will seek a doctor’s help.