Are you experiencing pain or discomfort at the base of your thumb and is the pain bothering you in doing your daily activities? Let’s walk through a quick guide on understanding thumb arthritis.
What is a Thumb Arthritis Test?

A thumb arthritis test is performed by doctors to evaluate the joint condition at the base of the thumb also known as the carpometacarpal joint (CMC joint). The result would be considered positive if the patient experienced pain during the examination that would confirm thumb arthritis.
CMC joint or thumb arthritis is distinguished by joint cartilage deterioration that causes bone to bone grinding due to a lack of bone cushion which results in pain, inflammation, and limited range of movement. Thumb assessment involves moving the thumb around and adding pressure against the base of the thumb or wrist area while looking out for grinding sounds or painful areas that would suggest cartilage wear.
There are four stages of thumb arthritis/osteoarthritis according to the Eaton-Litter classification.
| Stage | Radiographic description |
| Stage 1 | slight CMC joint space widening |
| Stage 2 | slight CMC joint space narrowing with sclerosis and cystic changes, presence of osteophytes (bone lumps that grow on bones or around joints), and loose bodies < than 2 mm |
| Stage 3 | advanced CMC joint space narrowing, sclerosis, cystic changes, presence of osteophytes or loose bodies > 2 mm |
| Stage 4 | arthritic changes in the CMC joint as in Stage 3 with scaphotrapezial arthritis |
Demographics
The hands and the hips are the second most affected areas by osteoarthritis next to the knee joints. Arthritis of the thumb joint is predominantly seen in women more than men and is associated with aging. Other risk factors include patients with a family history of arthritis, overweight, menopause, joint laxity, occupational exposure, and previous joint injury. A meta-analysis study reported the radiographic prevalence rate of thumb base arthritis for 50-year-old male and female patients was 5.8% and 7.3%, respectively.
Diagnosis, signs, and symptoms
Signs and symptoms include pain, grasp and pinch weakness, inflammation, thumb base discomfort, and limited joint mobility. Doctors would perform the following to properly diagnose thumb arthritis:
- a physical examination to check for swelling, stiffness, deformity, and instability
- joint palpation while checking for pain
- a detailed medical history interview
- radiographic imaging to confirm the severity of thumb arthritis based on the Eaton-Litter classification (including joint space narrowing, presence of osteophytes, and bone changes).
How can I test for thumb arthritis at home?
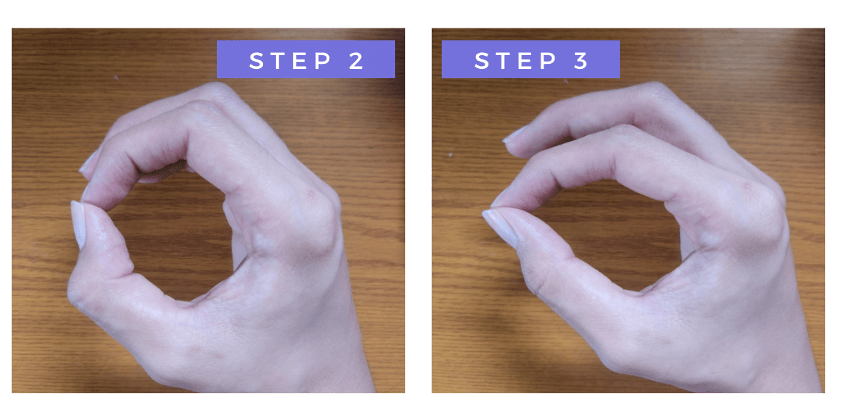
One short and easy way of testing thumb arthritis at home is the O and D shape test. Follow the steps numbered below:
- Touch the tip of your thumb using the tip of your index finger.
- If you notice an O shape, your thumb is normal (no arthritis).
- If you notice a D shape, this is a possible sign of thumb arthritis.
Other physical tests that doctors perform are:
- grind test
- traction-shift test
- pinch strength
- lever test
- metacarpal flexion test
- metacarpal extension test
The grind test is a commonly used evaluation test to confirm osteoarthritis by applying compression pressure to the patient’s metacarpal thumb bone while moving it around the metacarpal thumb base. A positive test would result in sudden pain in the CMC joint with or without crepitus (harmless clicking joint sounds). Although this test is a good clinical assessment, it is recommended that this exam would not confirm milder cases of thumb arthritis. Hence, further radiographic imaging may be suggested.
Traction-shift test is similar to the grind test in which pressure is applied using longitudinal pulling to the thumb to induce partial dislocation and relocation of the basal thumb joint. A positive result would cause pain within the CMC joint.
A pinch strength test involves the use of a pinch gauge dynamometer that measures a patient’s key pinch, lateral pinch, and tripod pinch in comparison to the unaffected hand.
Another provocative maneuver is the lever test also known as the pressure-shear test. This test is performed by gripping the first metacarpal after the basal thumb joint and applying force while rocking it back and forth.
The metacarpal flexion test is done by adding a firm downward force to resist the patient’s flexion of the thumb. Similarly, the metacarpal extension test is done the same way by resisting the extending thumb. The test is positive if it produces pain.
Sensitivity and Efficacy rates
A study with sixty-two patients with basilar joint arthritis compared the diagnosis ability of the grind test, lever test, and metacarpophalangeal extension test. The lever test showed the highest sensitivity while the grind test displayed the lowest. However, above all tests, the grind test was observed to have the highest specificity.
Another study with 104 patients evaluated the accuracy of thumb arthritis diagnosis using the grind, lever, flexion, and extension test. The study reported sensitivity rates of 64% for the grind test, 99% for the lever test, 36% for the flexion test, and 46% for the extension test, and specificity rates were 100%, 95%, 100%, and 100%, respectively.
Other diagnostic tests
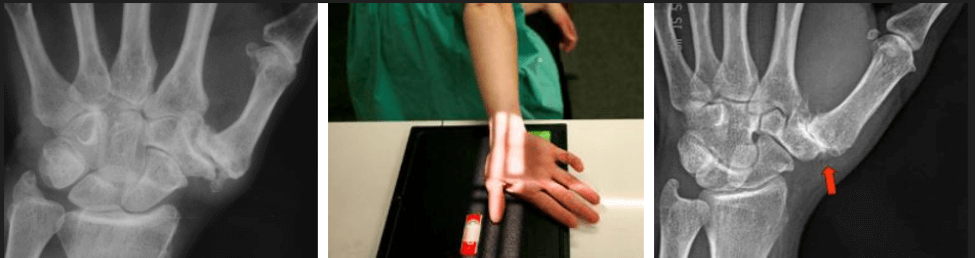
Photo by ORTHO BULLETS
Further imaging techniques such as X-rays and bone scans can be carried out to confirm the diagnosis and determine the current stage of thumb arthritis.
Treatment
Good news. There are conservative treatment options based on your stage and symptoms. However, if the conservative approach fails, surgical procedures may be of greater help to treat this condition. Nonsurgical treatment is recommended for less severe thumb arthritis which includes topical and oral anti-inflammatory medications, day-to-day activity modification, splinting, and injections. Surgical treatment strategies such as arthroplasty and arthrodesis are suggested for advanced thumb arthritis.
Medications
Non-steroidal antirheumatics (NSAR), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, and cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors medications for the reduction of pain can be used as conservative treatment in the early stages of thumb joint arthritis. Injection therapy treatment using hyaluronic acid or corticosteroid is also another effective intervention.
Surgery
Surgical treatments are often done in severe cases to relieve symptoms of patients who do not respond to the conservative approach. These surgical procedures include:
- Arthroplasty – also known as a joint replacement in which a full or partial joint removal is performed followed by replacement with implants or tendon graft.
- Arthrodesis – also known as joint fusion in which bone joints are surgically fused.
- Osteotomy – this procedure reshapes then realigns/repositions the affected bone/joint
A variety of results ranging from early surgical failure rates to great long-term successful procedures to treat basal thumb joint arthritis.
Lifestyle – home care, home remedies
Incorporating lifestyle changes and habits involving home care and exercises may greatly help in improving pain, physical function, range of motion and strength of the thumb.
Exercise/ therapy – discuss thumb/hand exercises for arthritis
Protecting the joints by using a thumb splint is a precautionary measure in doing daily activities like opening a jar or door, zipping and unzipping clothes, and writing. Splint type and the duration of wearing a splint will be greatly determined by your symptoms and by the assessment of your doctor. There are many splint variants to choose from in the market ranging from flexible, rigid non-custom, and custom thermoplastic fits. Also, using less force in gripping and grasping as well as using the unaffected hand alternately will also help. Massaging the muscles once in a while may relieve pain and prevent hand stiffness. Hand exercises like playing the piano, are recommended to strengthen the muscles around the CMC joint.
Which type of doctor specializes in thumb arthritis?
A rheumatologist is a doctor who specializes in bone, muscle, and joint diseases such as arthritis. If you are experiencing the symptoms listed above, consult with a rheumatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
How to book with a Rheumatologist on NowServing
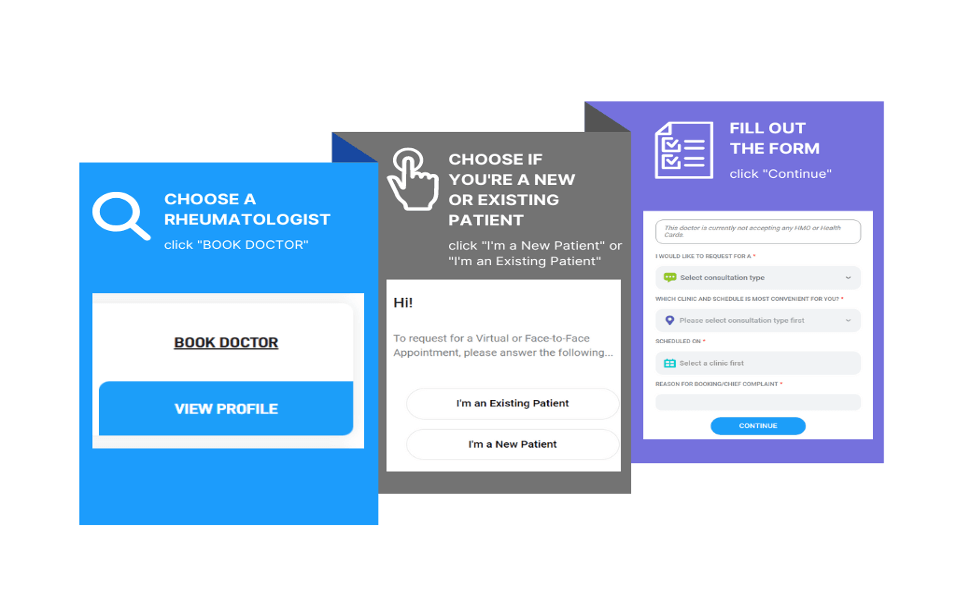
To book a consultation follow these simple steps:
- Click on this link.
- Choose a rheumatologist by clicking “BOOK DOCTOR”. You may also check your doctor’s credentials, educational background, and clinic schedule by clicking “VIEW PROFILE”.
- Select if you’re an existing patient or a new patient.
- Fill out the form and click continue.
- Review and confirm your consultation.
You can also download the app for a seamless experience.
How to prepare before the scheduled consultation
In preparing for your appointment you can list down the following:
- Description and onset of all your symptoms
- Medical history and medication allergies
- Questions to ask your doctor (like causes of your symptoms, further tests, treatment strategy, and management, etc.)
Summary
CMC joint arthritis is a serious condition that commonly affects the elderly population and causes significant pain and hindrance in daily tasks. Patients should closely monitor any signs of thumb discomfort, pain, swelling, inflammation, and stiffness. Schedule a consultation with your doctor for treatment strategies that would best work for you.
Careful physical assessment of the thumb using the listed thumb arthritis tests above as well as having further imaging tests may help to properly diagnose this condition. In the failure of conservative treatment, surgical intervention may be recommended by your doctor based on the severity of your CMC joint arthritis. Post-surgical procedures require adequate care and therapy to ease the pain and improve the quality of life. Early diagnosis and treatment are best to treat this troublesome condition.
If you suspect you may have thumb arthritis, there are a few simple tests you can do at home to help determine if this is the cause of your discomfort. One common test is the grind test, where you gently try to move your thumb in a circular motion while applying slight pressure. If this causes pain or a grinding sensation, it could be a sign of arthritis. Another test is the pinch test, where you try to pinch a small object between your thumb and fingers. If this is difficult or painful, it may also indicate arthritis. If you experience these symptoms, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.