When it comes to adult age, it is common to encounter conditions that affect the joints like rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This autoimmune disease can affect the daily activities of the patient due to noticeable swelling. That’s why it is a must to be aware of the common rheumatoid arthritis symptoms before it progresses to a severe illness.
In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of RA. Understanding the early warning signs of RA is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment. Let’s begin!
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
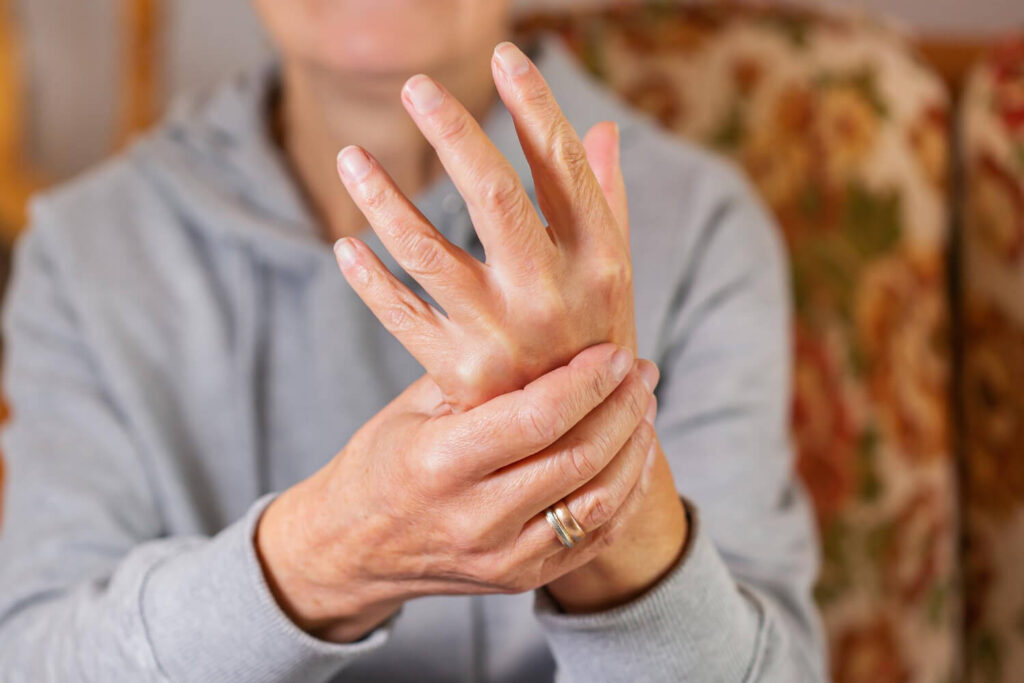
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the joints, leading to swelling, stiffness, and pain. The most commonly affected joint includes the small joints of the hands and feet. Aside from that the larger joints like the knees, shoulders, and hips can also be compromised. With such widely affected areas, flare-ups are to be expected as the symptoms worsen.
Identifying the Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Early detection of rheumatoid arthritis is crucial for effective management and to prevent further joint damage. By recognizing the early warning signs, individuals with suspected rheumatoid arthritis can seek medical attention promptly and begin the appropriate treatment plan.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. However, it is important to note that it can also manifest in other parts of the body, leading to a range of symptoms.
Joint Symptoms to Watch Out For
One of the hallmark signs of this condition is joint stiffness, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity. This stiffness may persist for over an hour and may be accompanied by joint pain, swelling, and warmth. In addition to these symptoms, individuals with early-stage may experience joint tenderness or a sensation of “creakiness” upon movement.
This illness typically affects multiple joints symmetrically, meaning that if one joint is affected, the corresponding joint on the other side of the body may be affected as well. Commonly affected joints include the hands, wrists, elbows, shoulders, knees, and ankles.
As the disease progresses, RA can lead to joint deformities, making it even more crucial to identify and manage the condition early on.
Non-Joint Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
While it primarily affects the joints, it can also manifest in other parts of the body. Fatigue is a common symptom experienced by individuals with RA, often due to systemic inflammation. The persistent inflammation in the body can lead to a feeling of exhaustion and low energy levels.
In addition to fatigue, individuals may experience other non-joint symptoms. Some instances include low-grade fever, loss of appetite, and a general feeling of malaise. The systemic inflammation can affect various organs, leading to complications in some cases. Thus, leading to potential health issues.
The Impact of Rheumatoid Arthritis on the Body
As mentioned, the rheumatoid arthritis can have widespread effect in the joints. However, as it worsens, it goes beyond by affecting the other bodily functions.
Let’s uncover the different chronic inflammation associated with the disease.
Cardiovascular Problems
When it comes to cardiovascular problems, individuals with RA have an increased risk of developing heart disease. The chronic inflammation in the body can damage the blood vessels, leading to atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque in the arteries. This can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Respiratory Problems
Respiratory issues are also a concern for individuals with this illness. The inflammation can affect the lungs, leading to conditions such as interstitial lung disease and pleurisy. These respiratory complications can cause shortness of breath, coughing, and chest pain, making it harder for individuals to engage in physical activities and affecting their overall quality of life.
Bone Problems
Furthermore, it can have a significant impact on bone health. The chronic inflammation can lead to bone loss, increasing the risk of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened and brittle bones, making individuals more susceptible to fractures. This can further complicate the management of the condition, as fractures can lead to additional pain and mobility issues.
Mental Health Problems
Mental health is another aspect that is often affected by the condition. The chronic pain, fatigue, and limitations imposed by the disease can take a toll on a person’s mental well-being. Depression and anxiety are common among individuals with RA, as they navigate the challenges of living with a chronic illness. It is important for healthcare providers to address the mental health needs of patients with RA and provide appropriate support and resources.
The Progression of Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms

RA symptoms can vary depending on the stage of the disease. Understanding the progression of symptoms helps individuals and healthcare professionals assess the severity of the condition and determine the appropriate treatment approach.
Early Stage Symptoms
In the early stages of RA, symptoms may be mild or intermittent. Joint stiffness and mild pain are common, often accompanied by fatigue and a general sense of unwellness. These early symptoms can come and go, leading to periods of remission, which may give individuals a false sense of improvement. However, without early intervention, RA can progress and cause more severe symptoms.
During the early stage of rheumatoid arthritis, individuals may also experience morning stiffness that lasts for more than an hour. This stiffness can make it challenging to perform daily activities, such as getting dressed or preparing breakfast. Additionally, some individuals may notice swelling and redness around the affected joints.
It is important to note that early diagnosis and treatment can significantly slow down the progression of RA. Therefore, individuals who suspect they may have rheumatoid arthritis should seek medical attention promptly to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Advanced Stage Symptoms
With the progression of the condition, it also produce advanced rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. These persistent signs may include joint pain and stiffness. Furthermore, swelling and inflammation of the joints may become more noticeable, which shows progressive joint damage and deformities. Severe RA can also lead to systemic complications, impacting overall health and well-being.
In advanced stages of rheumatoid arthritis, individuals may find it challenging to perform simple tasks such as opening jars, writing, or even holding a cup. The pain and stiffness can be constant, making it difficult to find relief. At this stage, the inflammation can affect multiple joints, including those in the hands, wrists, knees, and feet.
Moreover, the chronic inflammation can lead to the erosion of the joint cartilage and bone. This can result in joint deformities, such as swan-neck deformity or boutonniere deformity in the fingers. The impact of these deformities on an individual’s quality of life can be significant, affecting their ability to perform activities of daily living independently.
Furthermore, advanced RA can also affect other organs and systems in the body. It can cause inflammation in the eyes, leading to dryness, redness, and even vision problems. Additionally, individuals with severe RA may experience fatigue, weight loss, and a general feeling of malaise due to the systemic nature of the disease.
Given the potential complications and impact on daily life, it is crucial for individuals with advanced RA to work closely with their healthcare team to manage symptoms effectively. Treatment options may include a combination of medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to improve joint function and overall well-being.
Importance of Early Detection and Diagnosis
Early detection and diagnosis play a vital role in managing the disease effectively and slowing down its progression. Recognizing the rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and seeking medical evaluation allows healthcare professionals to initiate appropriate treatment strategies and interventions.
When RA is diagnosed early, individuals have a better chance of achieving remission or low disease activity. Once that happens, it significantly improves the quality of life of patients.
Benefits of Early Diagnosis
There are several benefits for individuals if early intervention begins. It allows for early intervention with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), which have been shown to slow down joint damage and preserve joint function. These medications work by suppressing the immune system’s abnormal response, reducing inflammation, and preventing further destruction of the joints.
In addition to medication, early diagnosis enables healthcare professionals to provide education and support, helping individuals manage RA-related symptoms and improve their quality of life. They can offer guidance on lifestyle modifications, such as exercise routines, joint protection techniques, and stress management strategies. Furthermore, early intervention allows for the implementation of physical and occupational therapy, which can help improve joint mobility, strength, and function.
Moreover, early diagnosis allows individuals to actively participate in their treatment plan and make informed decisions about their healthcare. It empowers them to engage in shared decision-making with their healthcare team, ensuring that their preferences and goals are considered in the management of their condition.
Diagnostic Tests for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Diagnosing RA involves a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history assessment, and laboratory tests. Healthcare professionals may conduct blood tests to check for specific markers, such as rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies. These markers are often elevated in individuals with RA and can help confirm the diagnosis.
Additionally, imaging tests, such as X-rays or ultrasounds, may also be utilized to assess joint damage and inflammation. X-rays can reveal characteristic changes in the joints, such as erosions and joint space narrowing, while ultrasounds can provide real-time visualization of joint inflammation and synovial thickening.
Furthermore, healthcare professionals may perform a thorough physical examination, assessing joint tenderness, swelling, and range of motion. They may also evaluate other clinical features, such as morning stiffness, fatigue, and systemic symptoms, to aid in the diagnosis of RA.
Diagnosing RA requires a comprehensive approach, involving collaboration between the individual, healthcare professionals, and specialized rheumatology teams. These tests introduced can help keep track of the phase of the condition. However, do take note that tests may still vary depending on the hospital you visit. It would be best to check with your hmo provider whether the needed tests are covered and available in that place.
Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis

Managing and treating RA requires a comprehensive approach. Treatment plans are typically tailored to each individual and may include a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and surgical interventions.
Medication and Drug Therapies
Medication plays a central role in RA treatment. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to manage pain and inflammation. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are prescribed to slow down disease progression and control symptoms. Biologic agents, a type of DMARD, target specific components of the immune system involved in RA. In more severe cases, corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation quickly. It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to find the most appropriate medication regimen.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
In addition to medication, certain lifestyle changes can help individuals manage RA symptoms. Regular exercise is essential to maintain joint mobility and muscle strength. Physical and occupational therapy can aid in learning techniques to alleviate pain and protect joints. Applying heat or cold packs, using assistive devices, and practicing relaxation techniques may also provide relief. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can support overall health and reduce inflammation.
Surgical Interventions for Rheumatoid Arthritis
In cases where joint damage is severe and unresponsive to conservative treatments, surgical interventions may be necessary. Joint replacement surgery, such as knee or hip replacement, can relieve pain and restore joint function. Synovectomy, a procedure to remove the inflamed synovium, may be considered to alleviate symptoms. However, surgical interventions are typically reserved for advanced stages of RA when conservative measures have proven ineffective.
Conclusion
Recognizing the early warning signs of rheumatoid arthritis is crucial for early detection and timely intervention. The impact of RA on the body can affect several bodily functions, which might need surgical intervention. That’s why monitoring the condition is key to avoid its progression.
It is important for individuals experiencing any of these symptoms to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis. Slow down the progression of the disease by booking an online consultation with a rheumatologist for immediate intervention!