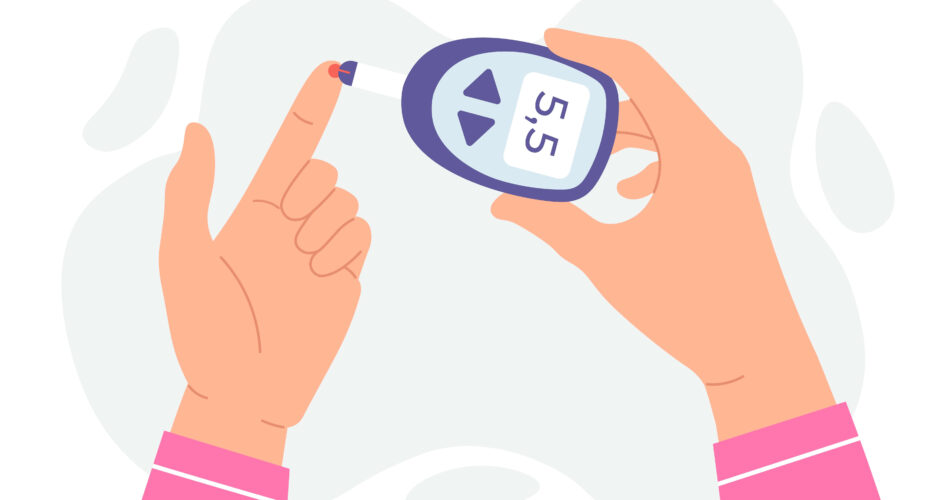
It’s crucial for women to prioritize their health. This side of the population are prone to having chronic diseases, one of which, is diabetes. Unfortunately, there are diabetes symptoms women don’t commonly recognize. Thus, resulting in the progression of the condition to the different types of diabetes.
Take charge of your well-being by recognizing the symptoms and understand how they may differ for women. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of diabetes, discuss its impact on the female body. Let’s begin!
What is Diabetes?

Diabetes occurs when the body either cannot produce enough insulin or cannot use it effectively. This leads to an accumulation of glucose in the blood, which can have serious health consequences if left uncontrolled.
When the body cannot produce enough insulin, it is known as Type 1 diabetes. This form of diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar levels.
On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or is unable to produce enough insulin to meet its needs. This is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for approximately 90% of all cases. Type 2 diabetes is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, lack of physical activity, and poor diet. It can usually be managed through a combination of medication, diet, and exercise.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy. It usually develops around the 24th week of pregnancy and typically resolves after childbirth. However, women who have had gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. It is important for pregnant women to monitor their blood sugar levels and follow a healthy lifestyle to manage gestational diabetes and reduce the risk of complications.
Understanding the different types of diabetes and their treatment options is crucial for effectively managing the condition and minimizing its complications. For accuracy about the current condition, patients are encouraged to visit a diabetology expert for a consultation.
The Female Body and Diabetes
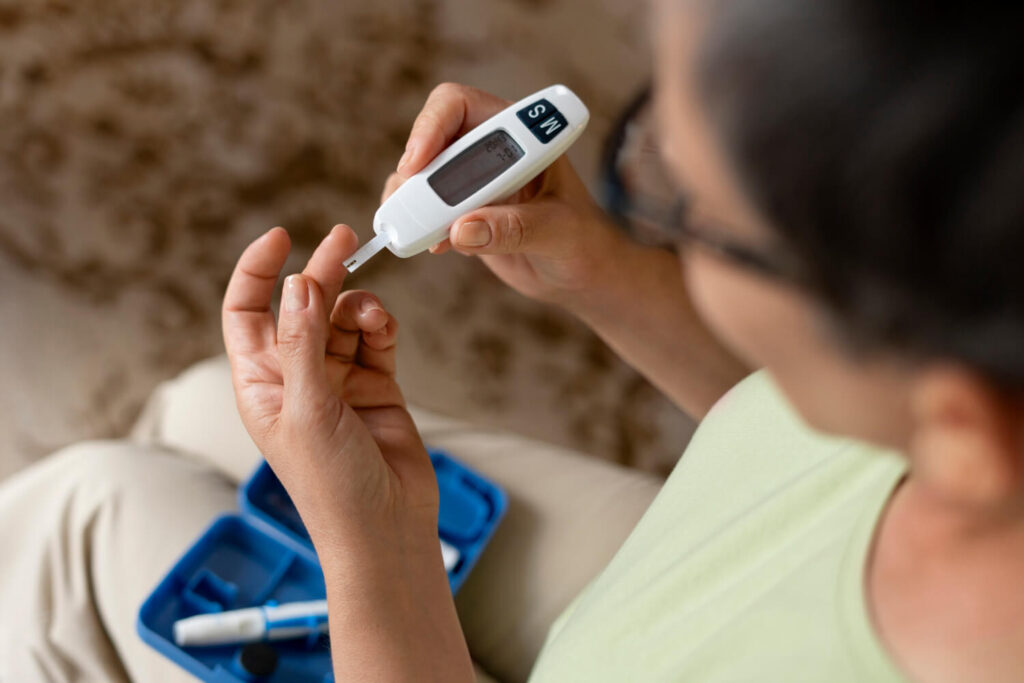

Now that we have a general understanding of diabetes, let’s explore how it affects women specifically. Diabetes can have unique complications and effects on the female body, including the role of hormones in the disease.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of women worldwide. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels, either due to the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or its inability to use insulin effectively. While both men and women can develop diabetes, there are certain aspects of the disease that are specific to women.
How Diabetes Affects Women Differently
Women with diabetes face specific challenges due to hormonal fluctuations, pregnancy, and issues related to reproductive health. These factors can influence blood sugar control and increase the risk of complications.
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during the menstrual cycle, can impact insulin sensitivity and blood glucose levels in women with diabetes. Many women experience higher blood sugar levels during certain phases of their menstrual cycle, which can make diabetes management more challenging.
Pregnancy also poses unique challenges for women with diabetes. Women who have diabetes before becoming pregnant, known as pregestational diabetes, need to carefully manage their blood sugar levels to ensure a healthy pregnancy. High blood sugar levels during pregnancy can increase the risk of birth defects and other complications.
Additionally, women with diabetes may face issues related to reproductive health, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or gestational diabetes. PCOS is a hormonal disorder that can affect insulin resistance and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes, on the other hand, occurs during pregnancy and typically resolves after childbirth, but it does increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
The Role of Hormones in Diabetes
Hormones play a vital role in diabetes management. Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels can affect insulin sensitivity and blood glucose levels. It’s crucial for women to be aware of these hormonal changes and adjust their diabetes management plan accordingly.
Estrogen, a hormone primarily associated with female reproductive health, has been found to have both protective and detrimental effects on diabetes. It has been suggested that estrogen may enhance insulin sensitivity and protect against the development of type 2 diabetes. However, during menopause, when estrogen levels decline, women may experience an increase in insulin resistance and a higher risk of developing diabetes.
Progesterone, another hormone involved in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy, can also impact blood sugar control. It has been observed that progesterone can reduce insulin sensitivity, leading to higher blood sugar levels in women with diabetes.
Understanding the role of hormones in diabetes is essential for women to effectively manage their condition. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, lifestyle modifications, and medication adjustments may be necessary to maintain optimal control.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Diabetes in Women

Early recognition of diabetes symptoms women is key to prompt diagnosis and effective management. Let’s explore the common symptoms below!
- Frequent urination, also known as polyuria, is a common symptom of diabetes. This occurs because high blood sugar levels cause the kidneys to work harder to filter and absorb the excess glucose. As a result, the bladder fills up more quickly, leading to more frequent trips to the bathroom.
- Increased thirst, or polydipsia, is another common symptom of diabetes. When blood sugar levels are high, the body tries to flush out the excess glucose through urine, which can lead to dehydration. As a result, you may feel an intense thirst and find yourself drinking more fluids than usual.
- Unexplained weight loss is often an early sign of diabetes. When the body is unable to properly use glucose for energy, it starts breaking down fat and muscle for fuel. This can result in unintentional weight loss, despite a regular or increased appetite.
- Feeling constantly fatigued is a symptom that many people with diabetes experience. The body’s inability to effectively convert glucose into energy can leave you feeling tired and lacking in energy throughout the day.
Unique Symptoms in Women
There are additional diabetes symptoms women related to their reproductive health. These symptoms should be taken seriously and discussed with a healthcare provider. Let’s discuss each of them below!
Vaginal Infections
Frequent vaginal infections, such as yeast infections, may be more common in women with diabetes. High blood sugar levels can create an environment in the vagina that is conducive to the growth of yeast and other bacteria, leading to recurrent infections.
Infection in the Urinary Tract
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can also be more common in women with diabetes. The excess glucose in the urine can provide a breeding ground for bacteria, increasing the risk of UTIs. Symptoms of a UTI may include a frequent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine.
PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects many women with diabetes. PCOS can cause irregular menstrual periods, excessive hair growth, acne, and difficulty getting pregnant. It is important for women with diabetes to be aware of the potential link between PCOS and their condition.
It is worth noting that while these symptoms may be more common in women with diabetes, they can also occur in women without the condition. Therefore, it is always important to consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of diabetes can significantly impact the course of the disease and minimize the risk of complications. Regular check-ups and tests are essential for women to stay proactive and ensure their well-being.
How Early Detection Can Change the Course
With early detection, women can receive appropriate treatment and make necessary lifestyle changes to manage their diabetes effectively. This can reduce the risk of complications and improve overall quality of life.
For instance, early detection allows healthcare providers to intervene at the earliest stages of diabetes, enabling them to create personalized treatment plans tailored to the individual’s needs. These treatment plans may include a combination of medication, diet modifications, and exercise routines. By addressing the disease early on, women can better control their blood sugar levels and prevent the onset of complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
In addition, early detection empowers women to take charge of their health and make informed decisions about their lifestyle. They can learn about the importance of a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques that can help them manage their diabetes effectively.
Regular Check-ups and Tests for Women
Women should undergo regular check-ups that include blood sugar tests, cholesterol screenings, blood pressure checks, and kidney function evaluations. These assessments aid in detecting any abnormalities and taking timely action.
During these check-ups, healthcare providers can assess the individual’s blood sugar levels to determine if they are within the normal range or if there are any signs of diabetes. Cholesterol screenings can help identify any lipid abnormalities that may contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease, which is common in individuals with diabetes. Blood pressure checks are crucial as high blood pressure can exacerbate the complications associated with diabetes. Kidney function evaluations are essential as diabetes can lead to kidney damage over time.
Furthermore, regular check-ups provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to educate women about the importance of self-monitoring their blood sugar levels at home. By using a glucometer, women can keep track of their blood sugar levels throughout the day and make adjustments to their treatment plan as needed. This self-monitoring allows for greater control over the disease and helps women stay proactive in managing their diabetes.
Managing Diabetes: Lifestyle Changes and Treatments
Once diagnosed with diabetes, implementing lifestyle changes and adhering to treatment plans become crucial for managing the condition. Let’s explore some effective strategies for diabetic women.
Healthy Eating Habits for Diabetic Women
A well-balanced diet with controlled carbohydrate intake is vital for managing blood sugar levels. A registered dietitian can help women create personalized meal plans that fit their lifestyle and health needs.
Exercise and Diabetes Management
Regular physical activity offers numerous health benefits for women with diabetes. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, helps maintain a healthy weight, and reduces the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Final Takeaway
It is essential for women to prioritize their health and stay proactive in managing their diabetes. Regular check-ups and tests play a vital role in detecting any abnormalities and taking timely action.
Detecting the disease early on, so women can make necessary lifestyle changes and reduce the risk of complications. Book an online consultation with a diabetologist to analyze your current condition.



