Brittleness and constant fractures in the bone indicate that the bone density is decreasing. When that happens, the patient is on the verge of developing osteoporosis. During its occurrence, patients may notice pain and other changes in bone health. Thus resulting in pain in some regions of their bodies, which if continues to be fragile can lead to fractures.
That’s how crucial it is to understand bone density for managing bone health. In this article, we’ll be discussing the role of bone density in the development of osteoporosis. At the same time, learn about how it occurs and how to prevent it. Let’s begin!
What Is Bone Density?
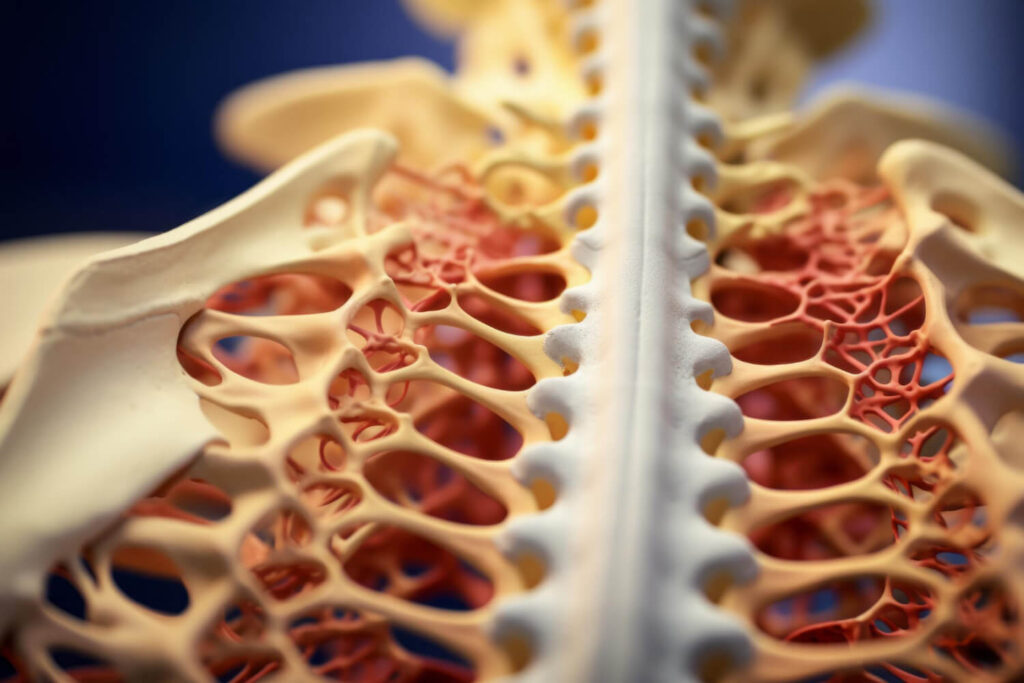
Bone density refers to the amount of minerals, primarily calcium, present in the bones. It is a measure of the strength and density of bones. The mineral content in bones determines their density and strength. Bones with higher mineral content are denser and less likely to break. On the other hand, bones with lower mineral content are less dense and more prone to fractures.
The mentioned scenarios are influenced by several factors, including genetics, age, gender, and lifestyle. During childhood and adolescence, density of the bones increase as they grow and develop. By the age of about 30, the peak is reached. After that, bone mass begins to decline gradually. Thus, increased bone fragility, leading to a higher risk of fractures occur.
The Link Between Bone Density and Osteoporosis
Low bone density is a key risk factor for osteoporosis. When bone density decreases significantly, the risk of developing osteoporosis increases. Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by weak and brittle bones, making them more susceptible to fractures.
Individuals with low density have a higher risk of bone fractures, even from minor falls or injuries. Fractures commonly occur in the spine, hip, and wrist. These fractures can lead to pain, disability, and a decrease in overall quality of life.
Maintaining optimal density of the bone is crucial for overall bone health and preventing conditions like osteoporosis. It is important to note that not everyone with low bone density will develop osteoporosis. However, having low density does increase the risk of developing the disease. Regular bone density testing can help identify individuals at risk and allow for early intervention and treatment.
Identifying Key Risk Factors
Several risk factors contribute to decreased density and an increased risk of osteoporosis. By identifying these risk factors, individuals can take proactive measures to maintain strong bones and prevent bone loss.
Age
This primary risk factor involves the natural declining of bone mass during aging. As people age, the minerals like calcium decreases leading to weak bones. That’s why most patients suffering from osteoporosis are seniors. In short, it puts older adults at higher risk of osteoporosis.
Gender
Meanwhile, another contributing risk is the patient’s gender. Commonly, women are more prone to osteoporosis due to hormonal changes during menopause. When they reached that certain stage in life, it can compromise their bone health. Even though women patients mostly develop it, men can have osteoporosis. Hormonal imbalances, such as low estrogen levels in women and low testosterone levels in men, can contribute to decreased density of the bone.
Lifestyle
On the other hand, patients can also have a decline in the density of the bone through poor lifestyle choices. That includes smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, a sedentary lifestyle, and a poor diet lacking in calcium and vitamin D can also contribute to decreased bone density. By understanding these risk factors and making positive lifestyle changes, individuals can mitigate their risk of decreased bone density and osteoporosis.
So, if you think your case can potentially lead to osteoporosis, you might want to visit a health expert to guide you on what to do. These experts specializes in bone health, which means they are also knowledgeable on how to check the current bone density of their patients. Set an appointment immediately to begin managing your bone health.
Understanding How to Measure Bone Density
In terms of measuring bone density, health experts can introduce various methods. The most common being a bone density test or dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan. Let’s discuss it below!
Bone density testing, including DXA scans, is an essential tool in evaluating bone health, diagnosing osteoporosis, and determining the risk of fractures. It allows healthcare providers to assess bone health and determine the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Thus, helping to maintain or improve bone density.
A DXA scan is a safe and non-invasive test that measures the mineral density of bones, primarily in the hip and spine. During the scan, the patient lies on a padded platform while a mechanical arm scans the targeted areas. The test uses low levels of radiation to assess the amount of calcium and other minerals present in the bones.
Results of the scan are measured in T-scores and Z-scores. T-scores compare an individual’s bone density to that of a healthy young adult of the same sex. Here’s how to easily understand T-scores:
- T-score of -1 or above indicates normal density
- T-score between -1 and -2.5 suggests osteopenia
- T-score of -2.5 or below indicates osteoporosis
On the other hand, Z-scores compare an individual’s bone density to that of individuals of the same age, sex, weight, and ethnicity. Z-scores are particularly useful in assessing bone health in children and premenopausal women.
Medications and Treatments for Managing Bone Density
Common Medications Prescribed for Osteoporosis
There are several medications commonly prescribed for the management of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by low density and increased fracture risk.
Bisphosphonate
One of the most common prescribed medication is Bisphosphonate. It is a class of medication that slows down bone loss and help maintain bone density. The medication works by inhibiting the cells responsible for breaking down bone. Commonly prescribed bisphosphonates include alendronate, risedronate, and ibandronate.
Hormone Therapy
Aside form that. experts also prefer hormone therapy as a form of medication treatment. Typically estrogen or estrogen-progestin combinations, may be prescribed to postmenopausal women. It can help prevent bone loss and reduce the risk of fractures. Thus, allowing bone strength to increase.
SERM
Meanwhile, another treatment is SERM, also known as, Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator (SERM). It is another class of medication used to prevent bone loss and reduce fracture risk. Raloxifene is a commonly prescribed SERM.
Vitamin D and Calcium Supplements
Lastly, supplement medication is one of the most crucial form of treatment for patients. So, it is expected for doctors to prescribe vitamin D and Calcium supplements. Consuming such medication can ensure adequate levels of these essential nutrients for bone health.
Take note that before getting the medications, it is best to consult a health expert first. That way, the correct dosage and length of usage will be tailored depending on the patient’s health status.
Diet & Lifestyle
Another form of treatment is the change in diet and lifestyle choices. People of your age possibly needs other assistance aside from medication, and changing these habits can help. A balanced diet and healthy lifestyle play crucial roles in maintaining strong bones and managing bone density. Here are some key considerations:
Diet Choices
- Include calcium-rich foods in your diet, such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods.
- Ensure adequate vitamin D intake through sunlight exposure and supplements.
- Avoid excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption, as they can interfere with calcium absorption.
Lifestyle Choices
- Engage in regular physical activity, particularly weight-bearing exercises like walking, jogging, and strength training.
- Maintain a healthy body weight to reduce the strain on your bones.
- Quit smoking, as it can negatively impact bone health.
By following a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and making other healthy lifestyle choices, you can support optimal bone health and reduce the risk of bone loss and fractures. Older women and men may find these challenging due to low endurance. So, it is ideal to visit experts to guide you in this bone health journey.
Conclusion
Maintaining strong bone density is crucial for overall health and preventing conditions like osteoporosis. Understanding the link between bone density and osteoporosis can help you take proactive measures to support your bone health. From lifestyle adjustments to appropriate medications and therapies, there are various ways to manage and improve bone density.
If you are currently suffering from this type of condition, it is never too late to manage your bone density. Prevent the progression of this problem into a full blown osteoporosis. Book an online consultation or visit the local health centers for a check up with a rheumatology doctor.
Bone Density Quiz
Test your knowledge about bone health and osteoporosis
Quiz Complete!
Concerned About Your Bone Health?
Get a bone density screening and consult with a specialist to assess your risk for osteoporosis.
Book Osteoporosis ScreeningFind a Specialist
Consult with an endocrinologist or rheumatologist for personalized bone health advice.
Find a Doctor