A common threat like atopic dermatitis has been one of the most misunderstood skin conditions. This health condition affects millions of people worldwide, and sadly, most still don’t know how to manage flare-ups, itchiness, and other symptoms. Other times, patients are clueless that their itchy skin is already a sign of dermatitis until the condition is in its later stages.
In this article, we aim to provide an overview of atopic dermatitis and how it can impact overall health when not managed early on. Discover the common signs and suitable treatment in this comprehensive guide. Let’s begin!
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis
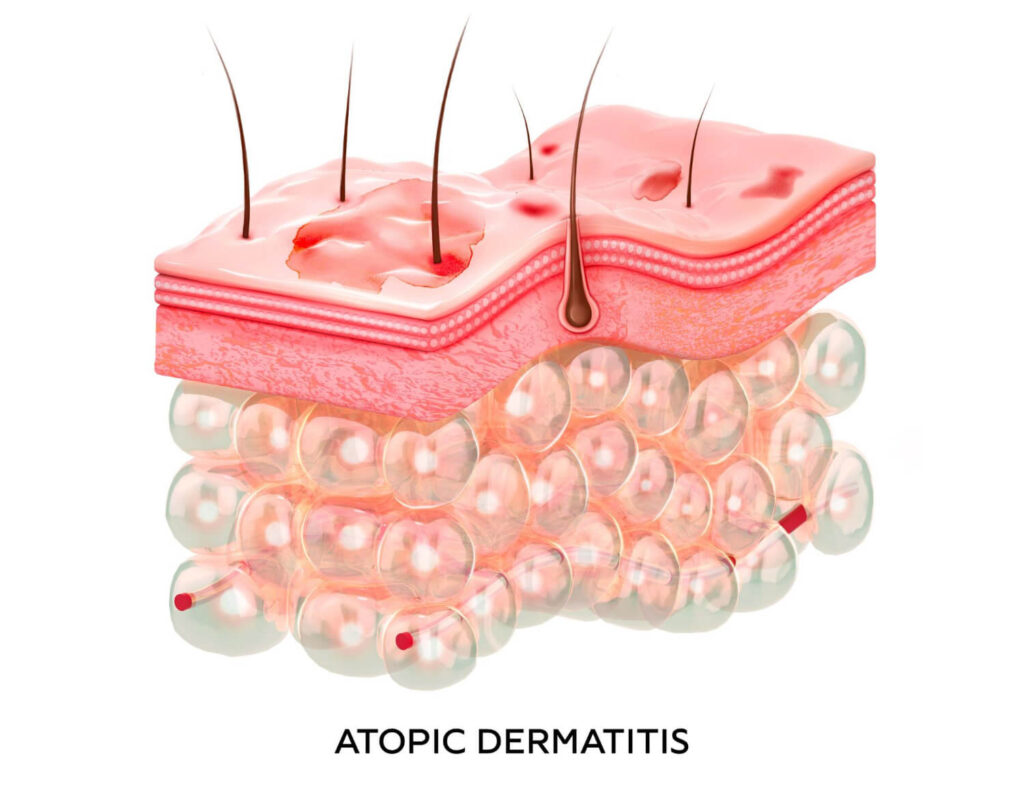
Atopic dermatitis is one of the types of eczema characterized by inflamed skin with a core of itch that can’t be scratched. Most people call it eczema as it is the most common type of eczema, while the other types are identified using their designated terms. Eczema is a known chronic condition that typically starts in childhood and may continue into adulthood. Despite that, the severity and frequency of flare-ups can vary from person to person. Some individuals may suffer greatly as young children and eczema flares disappear when they become teenagers.
Living with atopic dermatitis can be challenging, as the persistent itching and discomfort can impact daily activities and quality of life. The condition often leads to disrupted sleep patterns, emotional distress, and social withdrawal, especially in severe cases. In short, overall health can get disrupted when a person doesn’t face this health risk early on. Consequences in skin health and other bodily systems are affected. So, it’s best to monitor threats that may be a sign of atopic dermatitis occurrence.
Other Types of Eczema
- Contact Dermatitis
- Dyshidrotic Eczema
- Hand Eczema or Hand Dermatitis
- Neurodermatitis
- Nummular Eczema
- Stasis Dermatitis
Causes of Atopic Dermatitis
The first step in understanding atopic dermatitis is knowing the common factors that result in its development. Like any other type of eczema, atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition that results from a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
Individuals with atopic dermatitis often have a family history of allergic conditions like asthma or hay fever, suggesting a genetic component. Meanwhile, environmental factors such as exposure to certain allergens, irritants like tobacco smoke, or extreme temperatures can trigger or worsen symptoms. These irritants enter the protective barrier of the skin, which leads to skin infections, inflammation, etc.
When it comes to the immune system, it commonly overreacts to certain triggers that lead to inflammation and skin irritation. This hyperactive immune response can result in the skin barrier becoming compromised. Thus, making the patient more susceptible to allergens and irritants.
Recognizing Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
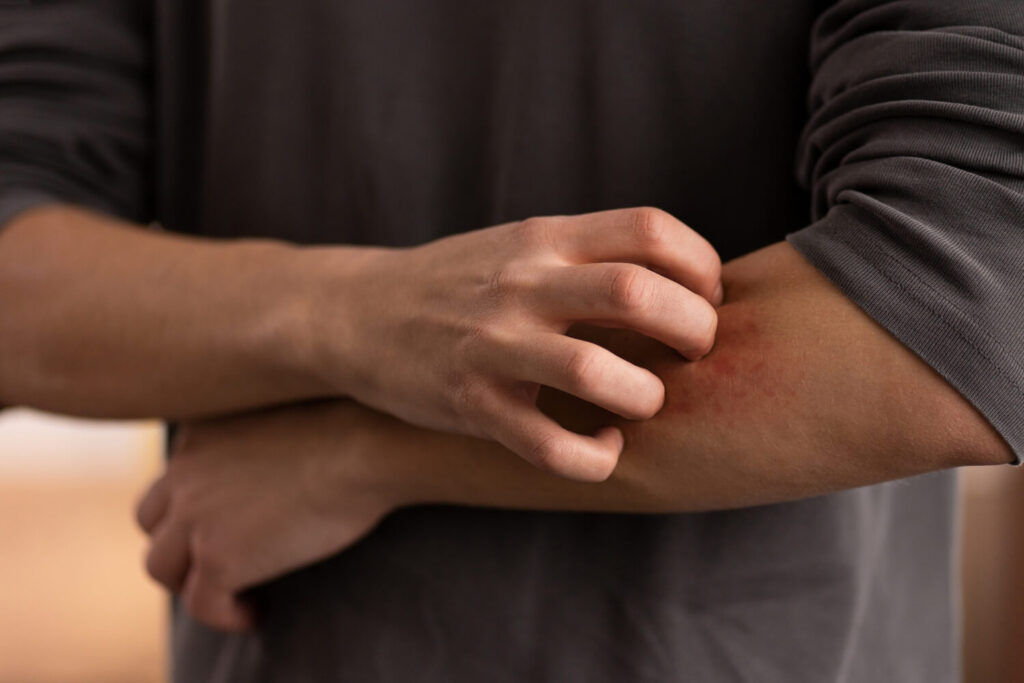

Individuals can monitor their health by identifying the presence of symptoms. There are several warning signs of atopic dermatitis. Discover if these signs are apparent in your current condition to help you acknowledge your skin health.
Common Physical Indicators
- Persistent itching
- Dry, scaly, or cracked skin
- Redness and inflammation
- Small raised bumps or rash
- Oozing or crusting of affected areas
Atopic dermatitis can manifest at any age, but it is most commonly seen in children. If you have this kind of skin condition during your younger years, you may have atopic dermatitis. Furthermore, if your child is itching and has these signs, your child has it too.
Remember that scratching the area can worsen the situation as the patient may feel intense pain. It’s best to contact a health expert immediately to manage eczema correctly.
Associated Health Conditions
Aside from symptoms, patients must also be prepared as it is often associated with other allergic conditions, such as asthma, hay fever, or food allergies. Understanding this connection is essential as it can help healthcare professionals develop a comprehensive treatment plan and address any underlying issues that may worsen or trigger atopic dermatitis symptoms.
Individuals with atopic dermatitis may experience flare-ups triggered by certain factors like stress, dry skin, irritants, or allergens. Managing these triggers through lifestyle modifications and proper skin care can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Treatment Options for Atopic Dermatitis
Living with atopic dermatitis can be challenging, but there are various treatment options available to help manage symptoms and improve the overall quality of life. Treatment plans are often personalized based on factors such as age, symptoms, and the severity of the condition.
Topical Treatments
When managing atopic dermatitis symptoms, topical treatments play a crucial role. These treatments include moisturizers or emollients that help keep the skin hydrated, corticosteroid creams or ointments that effectively reduce inflammation, and calcineurin inhibitors that work to suppress the immune response. In some cases, prescription-strength medications like antibiotics or antihistamines may be prescribed to treat secondary infections or alleviate itching.
Oral Medications
However, in more severe cases or when topical treatments are not sufficient, systemic medications may be necessary. These medications are taken orally and include corticosteroids, which help control inflammation. Oral immunosuppressants are also used to modulate the immune response, while biologic drugs target specific molecules involved in the inflammatory process.
Phototherapy
In addition to topical and systemic treatments, other options can help individuals with atopic dermatitis. One such option is phototherapy, also known as light therapy. This treatment involves exposing the affected skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial ultraviolet light. By doing so, phototherapy helps reduce inflammation and suppress immune system activity, leading to improved symptoms and skin healing.
Other Treatments
Furthermore, there are additional treatments that may be recommended to manage symptoms and promote skin healing. These include wet dressings, which involve applying wet bandages to the affected areas to soothe and hydrate the skin. Bleach baths, on the other hand, can help reduce bacterial colonization on the skin, thereby minimizing the risk of infection. Lastly, relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, may be suggested to help individuals cope with the emotional stress that can accompany atopic dermatitis.
Managing Atopic Dermatitis
While the treatment plan provided by the doctor can work to address the symptoms of atopic dermatitis, it is not enough to treat the condition fully. That’s why management tips are vital to keep the symptoms at bay. Below are some of the effective ways to manage the condition better.
Daily Skin Care Routine
A proper skincare routine is integral to managing atopic dermatitis. This involves using gentle, fragrance-free cleansers, moisturizing the skin regularly, and avoiding harsh or irritating substances. It is essential to understand individual triggers and make necessary adjustments to prevent flare-ups.
When it comes to moisturizing, it’s important to choose products that are specifically formulated for sensitive skin. Look for creams or ointments that contain ingredients like ceramides, which help restore the skin’s natural barrier. Lastly, applying moisturizer immediately after bathing or showering can help lock in moisture and prevent dryness.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Better Management
Lifestyle modifications can significantly impact atopic dermatitis. It is important to maintain a healthy and balanced diet. Avoiding potential allergens or irritants and incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation in the body.
Furthermore, choosing clothing made from breathable fabrics like cotton can help minimize irritation and allow the skin to breathe. Avoiding tight-fitting clothes or fabrics that trap heat and sweat can also help prevent flare-ups. Additionally, managing stress levels through relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises, yoga, or mindfulness meditation can have a positive impact on both physical and mental well-being.
Psychological Impact and Coping Strategies
Living with atopic dermatitis can have a psychological impact on individuals, including decreased self-esteem, anxiety, or depression. Seeking support from healthcare professionals or support groups can provide coping strategies, education, and emotional support to individuals and their families.
Connecting with others who are going through similar experiences can provide a sense of community and understanding. Support groups or online forums can be valuable resources for sharing tips, discussing challenges, and finding encouragement.
Conclusion
Atopic dermatitis or eczema is one of the chronic conditions that people must manage well. It affects patients from their younger years until adulthood. While some may experience milder consequences, individuals must still learn how to manage them well. With the mentioned treatment options and management tips, patients with this skin inflammation can improve their quality of life. At the same time, be proactive about achieving healthier skin despite the constant triggers around.
A combination of proper treatment methods and management tasks can help you achieve that. Book an online consultation or visit a local health center to meet with a dermatologist today!
Atopic Dermatitis Quiz
Test your knowledge about eczema symptoms and treatments
What is another common name for atopic dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is commonly known as eczema. It’s a chronic skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. While psoriasis, rosacea, and hives are also skin conditions, they have different causes and characteristics.
Which of the following is a common symptom of atopic dermatitis?
Dry, itchy skin is one of the hallmark symptoms of atopic dermatitis. The condition often causes intense itching that can lead to scratching, which may worsen inflammation and cause flare-ups.
What can trigger a flare-up of atopic dermatitis?
Stress, irritants, and allergens are common triggers for atopic dermatitis flare-ups. Other triggers include extreme temperatures, harsh soaps, certain fabrics, and environmental factors. Managing these triggers is key to controlling the condition.
Which treatment approach is commonly used for managing atopic dermatitis?
Moisturizers and topical corticosteroids are first-line treatments for atopic dermatitis. Regular moisturizing helps repair the skin barrier, while topical medications reduce inflammation during flare-ups. A dermatologist can create a personalized treatment plan.
Who is most commonly affected by atopic dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis most commonly begins in infancy and childhood, often appearing before age 5. However, it can affect people of all ages and may persist or develop in adulthood. Many children outgrow the condition, but some continue to have symptoms throughout their lives.