An autoimmune disease such as rheumatoid arthritis is a huge risk for a person’s health. Unfortunately, the rheumatoid arthritis causes is still unknown in the medical field. Still, that doesn’t mean there’s no way of managing it.
In this blog, we’ll help individuals to be more self aware of their condition for better understanding of the disease. Thus, ensuring they can monitor and address the illness before its progression. Let’s begin!
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis

Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by chronic inflammation of the joints. Unlike other types of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis, which is primarily caused by wear and tear on the joints, This type occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues, particularly the synovial membranes in the joints.
The synovial membranes play a crucial role in joint health. They produce a fluid called synovial fluid, which lubricates the joints and allows for smooth movement. In individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system targets these membranes, leading to inflammation and damage. Over time, this can result in joint deformities and functional limitations.
Unfortunately, this disease can affect multiple organs and systems in the body. Rheumatoid arthritis causes inflammation in other areas, such as the lungs, heart, and blood vessels.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can vary from person to person, but they often include joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, particularly in the hands, wrists, and feet. These symptoms are most pronounced in the morning or after a period of inactivity.
In most cases, rheumatoid arthritis causes symmetrical joint pain. That means it affects the same joints on both sides of the body. This is in contrast to other forms of arthritis, where joint pain may be localized to one side. The inflammation in this type of arthritis can also lead to warmth and redness around the affected joints. These symptoms are used for potential diagnosis by the health care expert.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing RA. Advancements in medical research can help individuals manage their symptoms and slow down disease progression. These treatments may include medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
The Role of Genetics in Rheumatoid Arthritis

This complex autoimmune disease is much common than most people think as it affects millions of people worldwide. The main cause is still not verified, but there are certain rheumatoid arthritis causes identified in some medical studies. One of them shown that genetics play a significant role in the development and progression of rheumatoid arthritis.
How Genetic Factors Influence Disease Progression
Genetic factors can impact the course and severity of the disease. Studies have identified specific genetic variations that are associated with more aggressive forms this illness. These variations may lead to increased inflammation, joint damage, and a higher risk of complications such as disability.
Usually, procedures such as genetic testing may help identify individuals at higher risk of developing RA and guide personalized treatment strategies. By identifying specific genetic variations, healthcare professionals can tailor treatment plans to target the underlying mechanisms of the disease. Thus, potentially improving outcomes and quality of life for patients.
Environmental Triggers of Rheumatoid Arthritis
It is important to note that while genetics play a significant role in RA, they are not the sole determinant of the disease. Other factors also contribute to the development and progression. Here are some of the identified triggers.
Smoking
One significant environmental factor that has been extensively studied is smoking. Research has consistently shown that smoking increases the risk of developing RA. Not only does smoking increase the likelihood of developing the disease, but it also worsens the severity of symptoms and joint damage. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can trigger an inflammatory response in the body, leading to the destruction of joint tissues. Quitting smoking is strongly recommended for individuals with RA, as it can help reduce disease activity and improve treatment outcomes.
Air Pollution
On the other hand, this environment factor has garnered attention in recent years. Pollutants can enter the body through inhalation and trigger inflammation, exacerbating existing rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. It is crucial to minimize their exposure to air pollution by avoiding heavily polluted areas and using air purifiers indoors.
Viruses and Infections
In addition to smoking and air pollution, infections and certain viruses have also been implicated as potential triggers of RA. It is believed that in individuals with a genetic predisposition to the disease, an infection or viral exposure can activate the immune system and trigger the autoimmune response.
Common infections, such as bacterial respiratory or urinary tract infections, have been associated with an increased risk of developing RA. The body’s immune response to these infections can mistakenly attack healthy joint tissues, leading to the development of RA. Furthermore, viral infections like Epstein-Barr virus and hepatitis C have also been linked to an increased risk of RA. These viruses can disrupt the immune system’s balance and trigger an autoimmune response.
Overall, understanding and minimizing these triggers is essential for managing the disease and improving the quality of life for individuals with RA. If cases involved results to the progression of rheumatoid arthritis, it’s best to seek help from a doctor immediately. Online consultations are available for emergency consultations as needed.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Rheumatoid Arthritis

The Influence of Diet and Nutrition
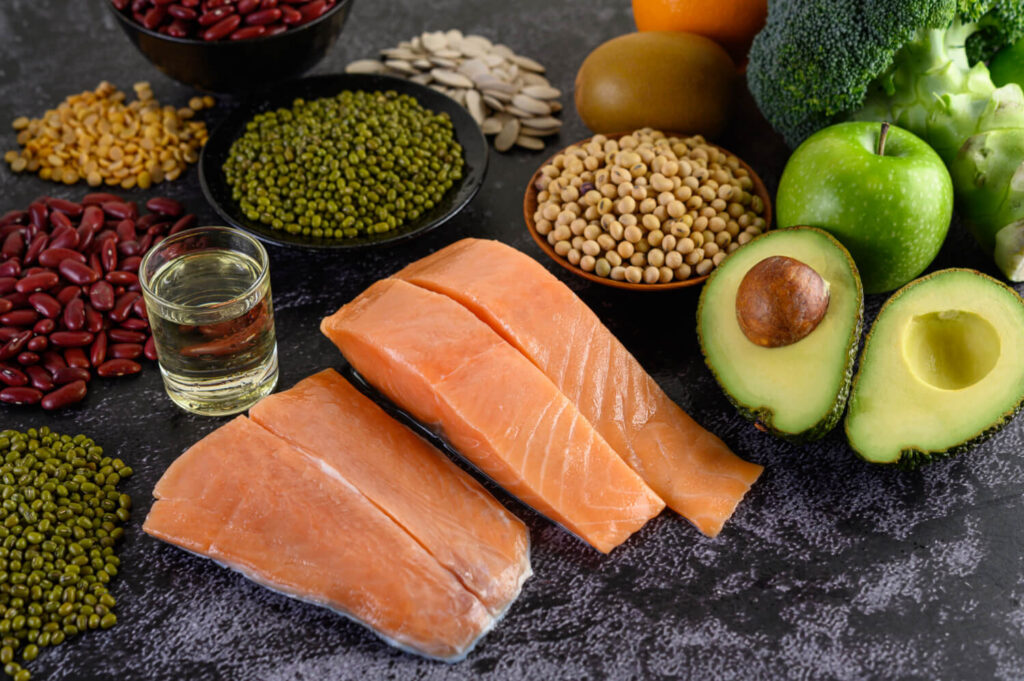
Diet and nutrition can significantly impact the development and management of rheumatoid arthritis. The foods we consume play a crucial role in our overall health, especially for people with the condition. Research has shown that certain dietary factors can either reduce the risk or help manage the symptoms of the disease.
One important dietary factor to consider is the consumption of omega-3 fatty acids. These essential fats are found in fatty fish, such as salmon and mackerel, as well as in nuts and seeds. Omega-3 fatty acids have been associated with a reduced risk of developing RA or experiencing a milder disease course. These healthy fats have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help alleviate the inflammation that is characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis.
Conversely, a diet high in saturated fats, processed foods, and sugary beverages can increase inflammation in the body and worsen symptoms. These unhealthy dietary choices can contribute to weight gain, which puts additional stress on the joints and exacerbates the pain and stiffness.
For patients, maintaining a well-balanced diet is crucial. This means incorporating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into their meals. Consulting with a diet and nutrition expert can be highly beneficial for individuals with it. Thus, helping individuals navigate any dietary restrictions or challenges that may arise.
The Impact of Stress and Mental Health

Aside from diet and nutrition, another possible conflict is the stress and mental health. It plays a significant role in the onset and progression of rheumatoid arthritis. The relationship between stress and rheumatoid arthritis, has been extensively studied. Chronic stress has been shown to contribute to systemic inflammation, which can trigger or worsen autoimmune responses in the body.
Living with a chronic illness like this type of arthritis can be emotionally challenging. The constant pain, fatigue, and limitations imposed by the disease can take a toll on mental health and overall well-being. It is not uncommon for individuals with the illness to experience feelings of anxiety, depression, or frustration.
Seeking support from healthcare professionals, friends, or support groups can provide individuals the opportunity to share their experiences, gain insights, and receive emotional support. Connecting with others who understand the daily struggles of living with it can be empowering and help individuals better cope with the disease.
Hormonal Factor in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Hormonal factors, particularly in women, have long been recognized as contributors to the risk and severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Women are two to three times more likely to develop the condition than men, and hormonal fluctuations throughout a woman’s life, such as during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can influence disease activity.
Estrogen, in particular, is thought to play a protective role against the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Women who undergo premature menopause or have lower estrogen levels may be at a higher risk of developing the disease. If progression occurs, it’s best to face the condition early on for immediate intervention and diagnosis.
Conclusion
It is important to note that rheumatoid arthritis causes are multifactorial. It can involve the genetics, lifestyle, and even other aspects, which normally triggers the development of this condition. By understanding this knowledge, managing the condition can be a lot easier for patients.
Unveil the key pillars for managing this chronic autoimmune disease. Book an online consultation with a rheumatologist.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Quiz
Test your knowledge about RA causes, symptoms, and management
Quiz Complete!
Concerned about joint pain?
Consult with a rheumatologist to get proper diagnosis and treatment for rheumatoid arthritis and other joint conditions.
Find a RheumatologistLearn more about Rheumatoid Arthritis
Explore our comprehensive guide on managing arthritis and gout for better joint health.
Read About RA