Arthritis is a common health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While many factors can contribute to the development of arthritis, one question that often comes up. That is whether it is hereditary or not. In this article, we will explore the genetic component of joint disorders as it shows why arthritis is hereditary.
The Role of Genetics in Arthritis

While factors can contribute to the development of arthritis, there is also a significant genetic component to consider. Studies have shown that genetics can play a major role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to developing arthritis. Therefore, supporting the claim that arthritis is hereditary, considering the relation between genes and the illness.
Arthritis is a complex condition that affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and inflammation. It can occur in various forms, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis. Understanding the role of genetics in arthritis can provide valuable insights into its development and potential risk to an individual.
Heredity and Arthritis: The Connection

When it comes to the hereditary aspect of arthritis, it’s important to understand that family history of the condition does not mean that an individual will develop arthritis. However, it does increase their risk compared to someone with no family history of the disease.
Defining if Arthritis is Hereditary
Having certain genes associated with arthritis does not guarantee that an individual will develop the condition. However, it does increase their susceptibility to developing it. Family history plays a crucial role in determining an individual’s risk. Certain genetic variations can be passed down from generation to generation.
Researchers have identified several specific genes that are associated with an increased risk of developing arthritis. These genes are involved in the regulation of the immune system and the inflammatory response. When these genes are altered or mutated, it can lead to an overactive immune response, causing inflammation in the joints and ultimately resulting in arthritis.
It is important to note that while these genetic variations increase the risk of developing arthritis, they are not the sole determining factor. Other factors, such as environmental and lifestyle factors, can also contribute to the development of the disease. For example, certain occupations that involve repetitive joint movements or exposure to toxins can increase the risk of developing arthritis, even in individuals without a family history of the condition.
The Role of Family History in Arthritis
If an individual has a close relative, such as a parent or sibling, with arthritis, their risk of developing the condition is higher compared to someone without a family history. This suggests that there is a hereditary component to arthritis. However, it is important to note that other factors, including environmental and lifestyle factors, can also contribute to the development of arthritis.
While certain genetic variations increase the susceptibility to arthritis, it is believed that environmental factors, such as exposure to certain infections or injuries, can trigger the onset of the disease in individuals with a genetic predisposition.
Understanding the connection between heredity and arthritis is crucial for both individuals at risk and healthcare professionals. By identifying individuals with a family history of the disease, healthcare providers can offer early intervention and preventive measures to reduce the risk of developing arthritis or manage the symptoms effectively.
Non-Genetic Factors Contributing to Arthritis
While genetics certainly play a role in the development of arthritis, it is not the sole determining factor. Other non-genetic factors can also contribute to the onset of arthritis.
Environmental Factors and Arthritis
Environmental factors such as exposure to certain toxins or infections can trigger an immune response, leading to joint inflammation and eventually arthritis. Additionally, occupational hazards, repetitive stress injuries, and traumatic injuries can also increase the risk of developing arthritis.
Lifestyle Factors and Arthritis

Lifestyle factors such as obesity, smoking, and physical inactivity can also contribute to the development of arthritis. These factors can put extra stress on the joints and lead to joint damage over time. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding smoking can help reduce the risk of arthritis.
Prevention and Management of Arthritis
While arthritis cannot always be prevented, there are strategies that individuals can adopt to reduce their risk and manage their symptoms.
Strategies for Arthritis Prevention
Avoiding or minimizing known risk factors for arthritis, such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and protecting the joints from injury, can help reduce the risk of developing the condition. Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods may also have a positive impact on joint health.
Understanding Arthritis
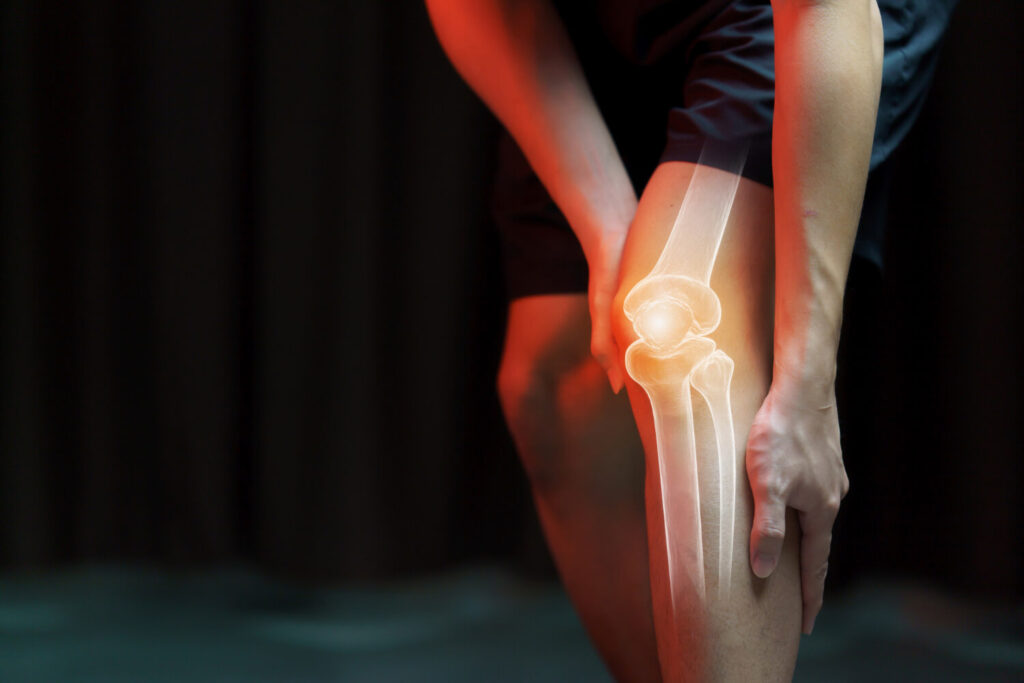
Before delving into the genetics of arthritis, it’s important to have a basic understanding of this condition. Arthritis refers to inflammation of the joints, which can cause pain, stiffness, and limited movement.
This chronic condition affects the joints, which are the points where two bones meet. The most common types of include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and others. Each type has its own unique set of symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, affecting millions of people worldwide. It typically occurs in older individuals, although it can also develop as a result of joint injuries or obesity. Osteoarthritis is characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, the protective tissue that covers the ends of bones in a joint. As the cartilage wears away, the bones may rub against each other, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Common risk factors for osteoarthritis include age, obesity, joint injuries, and repetitive stress on the joints. It commonly affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine. Treatment options for osteoarthritis include pain management, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and in severe cases, joint replacement surgery.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the joints. This leads to inflammation, pain, and swelling in the affected joints. Over time, the inflammation can cause damage to the cartilage and bones, leading to joint deformities.
Furthermore, rheumatoid arthritis can affect people of all ages, although it is more common in women and typically develops between the ages of 30 and 50. The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Thus, proving that arthritis is hereditary.
Gout
Gout occurs due to the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. Uric acid is a waste product that is normally excreted by the kidneys. However, in people with gout, the body either produces too much uric acid or has difficulties eliminating it. The excess uric acid can form sharp crystals that accumulate in the joints, leading to sudden and severe episodes of pain, swelling, and redness.
This disease primarily affects the big toe, but it can also occur in other joints such as the ankles, knees, wrists, and fingers. It is more common in men and is often associated with poor lifestyle factors.
It would be best to consult to an expert about the possible treatment for gout.
Other Types of Arthritis
In addition to the three most common types of arthritis mentioned above, there are several other forms of arthritis that can affect individuals. Psoriatic arthritis is a type of arthritis that occurs in people with psoriasis, a chronic skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches. Ankylosing spondylitis primarily affects the spine and can cause stiffness and pain in the lower back and hips. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis refers to arthritis that develops in children under the age of 16 and can have various subtypes.
Each type of arthritis has its own unique set of symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options. It is important for individuals with arthritis to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals.
Final Verdict
Arthritis has a strong genetic component, but it is not completely determined by one’s genes. Environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and other non-genetic factors also play a significant role in the development of arthritis.
By understanding the complex interplay between genetics and other factors, individuals can make informed decisions to reduce their risk and effectively manage arthritis if they develop the condition.
For individuals who have already been diagnosed with arthritis, it is important for individuals to work closely with their healthcare providers. Schedule a consultation online for immediate action and prevention against arthritis.
Arthritis Awareness Quiz
Test your knowledge about arthritis and its hereditary factors



