One of the most misunderstood conditions is the urinary tract infection, Most people don’t understand how it is a prevalent illness, which can be contracted in various ways. Unfortunately, with the lack of knowledge about it, most people tend to disregard UTI symptoms. Thus leading to an infection and even a recurring UTI.
In this article, we’ll help individuals to learn more about this condition. This guide will also cover the potential signs, which are necessary to seek help from health experts. Let’s begin!
What is a Urinary Tract Infection?
A urinary tract infection, commonly known as a UTI, is a bacterial infection that affects any part of the urinary system. That includes the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys. The infection can occur in both men and women, so it’s best to be proactive when it comes to urinary health.
The Anatomy of the Urinary Tract
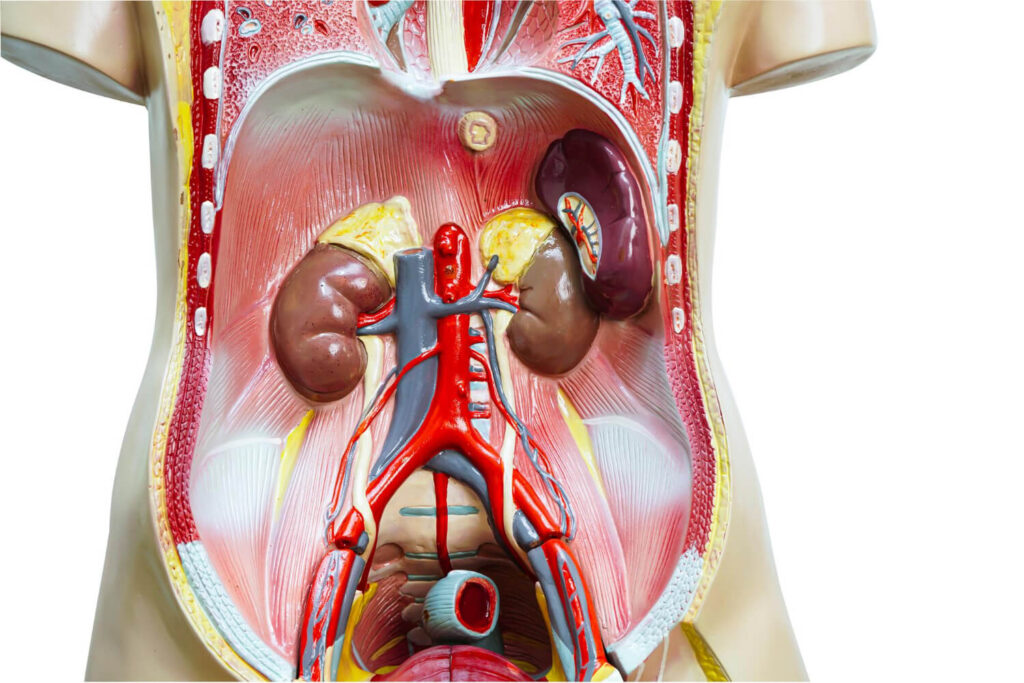
Before delving into the symptoms of UTIs, it’s essential to familiarize ourselves with the anatomy of the urinary tract. The urinary system consists of several components.
First of all is the kidneys, which play a vital role in maintaining the body’s overall health. It doesn’t only filter waste products but also help regulate blood pressure. This organ produces red blood cells, and maintain electrolyte balance. Meanwhile, the ureters filter the blood from the kidney, which creates the urine. It then act as conduits, transporting urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
On the other hand, the next part, the bladder, accommodates varying volumes of urine. a It is a remarkable organ, which expands and contracts to be the reservoir. Finally, the urethra serves as the exit route for urine. It is a tube that where the urine travels to be expelled from the body.
These parts are well connected to fulfill the needed process in the urinary system. However, with the influence of infection, it can affect everything leading to pain and inconvenience.
Common Causes of UTIs

When it comes to UTIs, there are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing an infection. For instance, sexual activity can introduce bacteria into the urethra, making women more susceptible to UTIs. Additionally, certain forms of birth control, such as diaphragms or spermicides, can also increase the risk of infection.
In men, an enlarged prostate can obstruct urine flow, leading to stagnant urine and an increased risk of UTIs. Furthermore, individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes or HIV/AIDS, are more prone to developing UTIs.
It’s important to note that while bacteria are the primary cause of UTI, other factors can contribute to their development. These common causes can significantly affect the urinary health. That’s why ensuring proper hygiene and preventing certain triggers can help avoid being infected.
Recognizing the UTI Symptoms

Identifying the uti symptoms is critical for prompt diagnosis and treatment. It is important to note that UTI symptoms can vary from mild to severe. Let’s discuss the common symptoms that people with UTI have been experiencing.
Physical Symptoms
Physical symptoms of a UTI often include:
- Pain or a burning sensation while urinating: This discomfort is caused by the inflammation and irritation of the urinary tract lining.
- Abdominal pain or discomfort: Some individuals may experience cramping or pressure in the lower abdomen.
- Cloudy or bloody urine: UTI can cause changes in the appearance of urine, making it appear cloudy or tinged with blood.
- Unpleasant odor in urine: In some cases, a strong and unpleasant odor may be present in the urine.
- Fever or chills: If the infection spreads to the kidneys, it can lead to a fever and chills.
- Fatigue or weakness: UTI can cause general feelings of fatigue or weakness due to the body’s immune response.
Changes in Urination
A UTI can also affect normal urination patterns, leading to:
- Frequent urination: Individuals with a UTI may feel the need to urinate more often than usual.
- Urgency to urinate: There may be a sudden and strong urge to urinate, even if the bladder is not full.
- Inability to urinate in large amounts: Despite the urge to urinate, only small amounts of urine may be passed.
- Strong and persistent urge to urinate: The feeling of needing to urinate may persist, even after emptying the bladder.
Systemic Symptoms
In addition to physical and urinary changes, some individuals may experience systemic symptoms, such as:
- Nausea or vomiting: UTI can sometimes cause nausea or vomiting, especially if the infection has spread to the kidneys.
- Pain in the lower back or sides: This type of pain may indicate a possible kidney infection, which requires immediate medical attention.
- Confusion or mental changes: Older adults with UTI may experience confusion or changes in mental status, which can be a sign of a more severe infection.
It is important to note that not all individuals will experience the same combination of symptoms, and some may have no symptoms at all. If you suspect you have a UTI, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
The Importance of Early Detection
Seeking early detection and treatment for UTIs is crucial for several reasons. For instance, untreated UTI can lead to more severe complications, such as kidney infections. Moreover, this condition can have a significant impact on kidney health. Recurrent UTI or untreated infection can contribute to the development of chronic kidney disease over time.
Furthermore, early detection and treatment of UTI can help prevent the spread of infection. This infection is typically caused by bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), entering the urinary tract. If left untreated, the bacteria can multiply and spread to other parts of the urinary system, leading to more severe infections.
It is important to note that certain individuals may be more susceptible to UTI, such as women, individuals with diabetes, pregnant women, and those with weakened immune systems. For these individuals, early detection and treatment are even more critical to prevent the potential complications associated with UTI. By seeking prompt medical attention and starting appropriate treatment, the spread of infection can be halted, reducing the risk of complications.
When to Seek Medical Help

Knowing when to seek medical help for a possible UTI is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Typically, it occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply, leading to infection. Thus, needed medical intervention is a must.
Here are some important factors to consider when deciding whether to seek medical help for a possible UTI:
Severity and Duration of Symptoms
If UTI symptoms are severe, which persists for more than a day or two, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. However, if symptoms such as fever, pain in the back or sides, or confusion are present, immediate medical attention is necessary. These could indicate a more severe infection that may require antibiotics or other medical interventions.
Recurrent UTI: When It’s More than Just Once
For individuals experiencing recurrent UTI, medical evaluation is recommended. Take note that frequent UTI may require additional tests to determine underlying causes and develop a proper treatment plan. Usually it is considered that case when the infection is recurring for at least 3 times in a year.
Recurrent UTI can be frustrating and disruptive to daily life. They may occur due to factors such as incomplete bladder emptying, urinary tract abnormalities, hormonal changes, or weakened immune system. By seeking medical help, healthcare professionals can assess the individual’s medical history, perform necessary tests, and recommend appropriate preventive measures to reduce the frequency of UTI.
Treatment Options and Prevention Strategies
Once a UTI has been diagnosed, the next step is to initiate appropriate treatment. UTI is typically treated with antibiotics, which work to eliminate the infection-causing bacteria. The choice of antibiotics depends on the type and severity of the UTI, as well as any known allergies or sensitivities the individual may have. Commonly prescribed antibiotics for UTI includes trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin, and nitrofurantoin.
It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by the healthcare provider, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished. This helps ensure that all bacteria are eradicated and reduces the risk of recurrent infections. In cases of recurrent UTI, a longer course of antibiotics or a different antibiotic may be necessary.
While antibiotics are crucial for treating UTI, preventive measures can also play a significant role in reducing the risk of infection. Maintaining proper hygiene practices, such as wiping from front to back after using the toilet and avoiding irritating feminine hygiene products, can help prevent the introduction of bacteria into the urinary tract. Staying well-hydrated is also important, as it helps flush out bacteria and promotes regular urination.
Conclusion
Understanding the UTI symptoms and knowing when to seek medical help can play a vital role in managing these common infections. By staying informed and taking appropriate action, individuals can ensure timely treatment, reduce the risk of complications, and maintain optimal urinary and kidney health.
Ensure proper management of the infection by following the guidance of health experts. Book an online consultation with a urologist to begin the health care initiatives.
UTI Symptoms Quiz
Test your knowledge about urinary tract infections
Quiz Complete!
Concerned About UTI Symptoms?
Consult with a healthcare professional to get proper diagnosis and treatment.
Find a Doctor for UTI