The bones are living tissues that constantly undergo a process of remodeling. Whenever old bones are broken, they are replaced with new ones. Throughout childhood and adolescence, the body produces more bone than it breaks down, resulting in a higher peak bone mass. However, as a person ages, their bones deteriorate, which results in osteoporosis. Thus, the balance between bone formation and resorption shifts, leading to a gradual loss of bone density.
That kind of change is a natural occurrence, which everyone should be prepared for. In this blog, we’ll uncover how this threat or condition can affect bone health, leading to lack of bone density. Discover the possible signs that you have developed this condition, and learn how to combat its effect on bone health. Let’s begin!
What is Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a condition that affects the bones, making them weak and brittle. It occurs when the creation of new bone cannot keep up with the loss of old bone, leading to a decrease in bone mass and density. This decrease in bone strength puts individuals at a higher risk of fractures, as even minor stresses or falls can cause the bones to break.
Several factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis. Women, especially older women who are past menopause, are at a higher risk due to the decrease in estrogen levels. Estrogen plays a crucial role in maintaining bone density. Other risk factors include a family history of osteoporosis, low calcium and vitamin D intake, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and hormonal disorders.
It is important to note that osteoporosis is often referred to as a “silent disease” because it typically does not cause any symptoms in its early stages. However, as the condition progresses and bone loss becomes more significant, symptoms may start to appear.
Understanding Bone Density and Its Importance
Bone density refers to the amount of mineral content in the bones and is an important indicator of bone health. It is often measured using a bone density scan, also known as a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan. This scan compares an individual’s bone density to that of a healthy young adult of the same gender. A lower T-score indicates a lower bone density and an increased risk of fractures.
With a low bone density, it indicates a deteriorating bone health, which is common during adulthood. That’s why most people develop conditions like osteoporosis, which is a painful bone conflict that people must combat immediately.
Common Areas to Develop Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis can affect various areas of the body, but some areas are more commonly affected than others. The most common areas to develop osteoporosis-related fractures include the hip, spine, and wrist. Let’s discuss each below!
Hips
Hip fractures are a significant concern for individuals with osteoporosis, as they can lead to significant disability and a reduced quality of life. These fractures often occur as a result of a fall and can require surgery to repair. The risk of hip fractures increases with age, and women are more likely to experience them than men.
Spine
Fractures in the spine, also known as vertebral fractures, are another common consequence of osteoporosis. These fractures can cause severe back pain and lead to a loss of height and a stooped posture. Vertebral fractures can occur spontaneously or due to minor trauma, such as bending or lifting. They can also result in a reduction in lung capacity and increased pressure on the abdominal organs.
Wrist
Meanwhile, wrist fractures are also a common occurrence in individuals with osteoporosis. These fractures often happen as a result of a fall on an outstretched hand, and they can cause significant pain and functional limitations.
Understanding the common areas affected by osteoporosis can help individuals recognize the potential signs and symptoms of the condition and take steps to prevent fractures.
Common Osteoporosis Symptoms

Osteoporosis often does not cause any symptoms in its early stages, which is why it is often referred to as a “silent disease.” However, as the condition progresses and bone loss becomes more significant, individuals may experience various symptoms.
In some cases, the first indication of osteoporosis may be a bone fracture that occurs with minimal trauma, such as a fall or even a cough. Recognizing these symptoms is important for early detection and appropriate management of osteoporosis.
Early Symptoms
In the early stages of osteoporosis, there may be no obvious symptoms. However, as bone loss progresses, individuals may start to experience certain signs that indicate the presence of the condition. These early symptoms can include:
- Back pain: Persistent or recurring pain in the back, often caused by fractures or collapsed vertebrae.
- Loss of height: A gradual decrease in height over time, which can be due to compression fractures in the spine.
These early symptoms may not be immediately noticeable or may be attributed to other causes. However, if you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and appropriate management.
Later Symptoms
As osteoporosis progresses, individuals may experience more noticeable symptoms that are often indicative of more advanced bone loss. These later symptoms can include:
- Broken bones: Fractures that occur with minimal trauma or even during everyday activities, such as bending over or coughing.
- Increased fracture risk: A higher likelihood of fractures, particularly in the hip, spine, and wrist.
- Hunched posture: A stooped or rounded upper back, which can result from compression fractures in the spine.
These later symptoms can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life and mobility. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience these symptoms, as early intervention and appropriate treatment can help manage the condition and reduce the risk of further fractures.
When to Visit A Health Expert
If you have risk factors for osteoporosis or are experiencing symptoms that could be indicative of the condition, it is important to consult a healthcare expert. They can evaluate your individual risk profile, conduct appropriate diagnostic tests, and provide guidance on managing your bone health.
Finding the Right Doctor
Finding the right healthcare provider is crucial for managing osteoporosis effectively. Here are a few tips to help you find the right doctor:
- Look for a healthcare provider who specializes in bone health and has experience in diagnosing and treating osteoporosis.
- Consider seeking a referral from your primary care physician or asking for recommendations from friends, family, or support groups.
- Check if the healthcare provider is board-certified in orthodontics, endocrinology, rheumatology, or another related specialty.
- Inquire about the doctor’s experience in treating patients with osteoporosis and their approach to treatment.
- Find out if these experts are accredited doctors of your HMO
Selecting a doctor who understands your specific bone health needs and works collaboratively with you is essential for effectively managing osteoporosis. Carefully assess your health and select the expert using the tips shared above.
Preparing for the Consultation
Preparing for a consultation with a healthcare provider can help ensure that you make the most of your appointment. Here are a few steps to consider:
- Gather relevant medical records related to your bone health.
- Make a list of questions or concerns you have about your condition, such as treatment options, lifestyle modifications, and potential side effects of medications.
- Write down any symptoms you have been experiencing and when they started.
- Be prepared to discuss your medical history, including any previous fractures, surgeries, or medical conditions.
By being prepared and actively participating in the consultation, you can ensure that you receive the necessary information and guidance to effectively manage your osteoporosis.
Understanding the Diagnosis Process
The diagnosis of osteoporosis is typically made through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. The most common test used to diagnose osteoporosis is a bone density scan, also known as a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan.
As mentioned, this bone density test allows the expert to analyze bone health by comparing it to a healthy young adult of the same gender. Once the T-score is revealed, the doctor can identify whether the case of osteoporosis is in its early stage or severe.
Whatever the case is, the health expert will discuss the result of the scan and create a suitable treatment plan for the patients. Although, there are also cases wherein the doctor will request additional tests.
Additional Tests and Scans for Osteoporosis
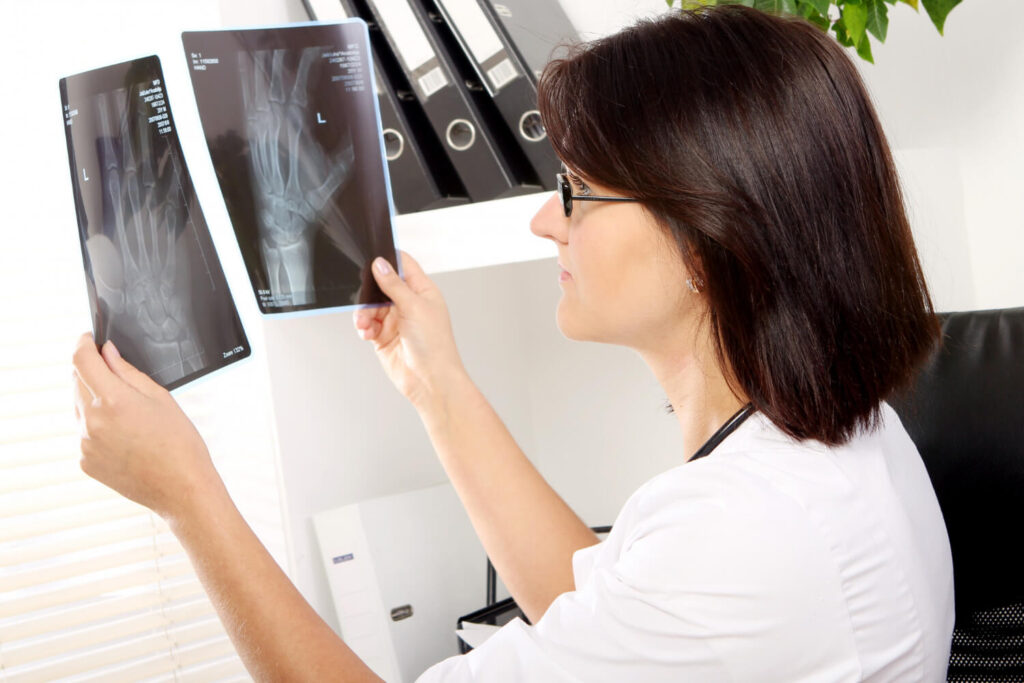
In addition to a bone density test, your healthcare provider may order other tests and scans to gather more information about your bone health and rule out other conditions. Some common tests and scans for osteoporosis include:
- Blood tests: These tests can measure hormone levels, such as parathyroid hormone, which play a role in bone health. Also, it can also help identify underlying medical conditions that may contribute to bone loss.
- X-rays: Detect fractures or changes in the bones that may indicate osteoporosis or other bone diseases.
- CT scans: It can provide detailed images of the bones and can help assess the severity of fractures or identify other bone abnormalities.
- MRI scans: Use magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the bones and soft tissues, allowing for a more comprehensive evaluation of bone health.
Afterwards, the doctor will discuss the possible conflict such as where the osteoporosis is visible. For instance, the results from the scans showed severe fractures, and that may have been a result of the low bone density. Every relevant factor will be discussed to let the patients know about their current bone health. Thus, allowing the patients to understand the possible threats of their condition.
During this stage, the patient is also encouraged to ask questions and clarify whenever they encounter some difficult topics. That way, they can understand osteoporosis fully.
Treatment Options for Osteoporosis
After the assessment, the health expert will come up with a suitable treatment plan. Treatment for osteoporosis aims to reduce the risk of fractures, relieve osteoporosis symptoms, and improve overall bone health. The treatment plan will depend on the severity of the condition, the presence of underlying medical conditions, and individual preferences. Common treatment options for osteoporosis include:
- Medication:
- Calcium and vitamin D supplements
- Rehabilitation and physical therapy
- Lifestyle modification
It is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and goals for treating osteoporosis.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy Approaches
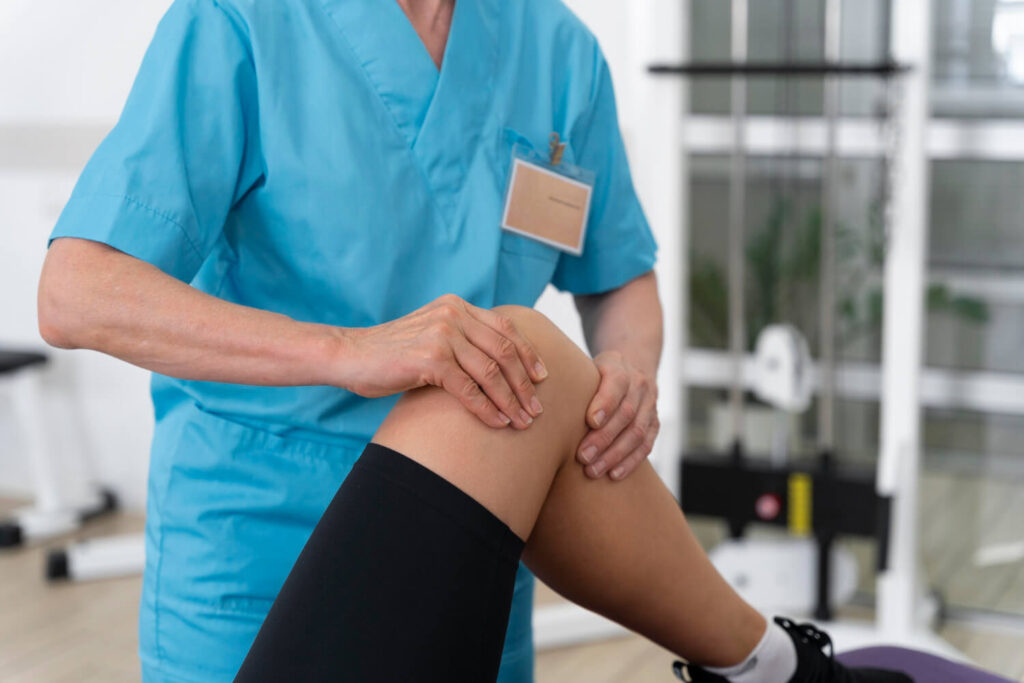

Rehabilitation and physical therapy can play a significant role in managing osteoporosis and improving overall bone health. These approaches focus on increasing physical activity, improving muscle strength, balance, and coordination, and reducing the risk of falls and fractures. Here are some rehabilitation and physical therapy approaches that may be beneficial:
- Physical activity: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can help improve bone density, muscle strength, and overall fitness.
- Tai chi: Tai chi is a low-impact exercise that involves slow, gentle movements combined with deep breathing. It can improve balance, flexibility, and muscle strength, reducing the risk of falls.
- Strength training: Resistance exercises using weights or resistance bands can help build muscle strength and improve bone density.
- Balance exercises: Specific exercises that target balance, such as standing on one leg or using a balance board, can help improve stability and reduce the risk of falls.
It is important to work with a qualified physical therapist or rehabilitation specialist to develop an individualized exercise program that is safe and appropriate for your specific needs and abilities.
Regular Check-ups and Professional Consultations
Attending regular follow-up appointments and consultations with healthcare professionals are essential for effectively managing osteoporosis and monitoring bone health. Doing so allows professionals to monitor changes in bone density and assess the effectiveness of treatment interventions. This can help identify any progression of the condition and guide adjustments to the treatment plan if necessary.
Furthermore, they can evaluate the need for continued medication use, adjust dosage if needed, and monitor for any potential side effects or interactions with other medications. This opportunity helps patients to manage their condition better, as they are guided by doctors. Thus, ensuring optimal bone health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the first signs of osteoporosis?
Loss of height, back pain, and easily fractured bones are common initial signs of osteoporosis. Pay attention to these symptoms as early detection is crucial in managing the condition effectively.
What is the possible age to develop osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis can develop at any age, but it is most commonly seen in postmenopausal women due to the decrease in estrogen levels. However, older adults, both men and women, can also develop osteoporosis as they age and experience age-related bone loss.
How to lower risk of developing osteoporosis?
Lowering the risk of developing osteoporosis can be achieved through various lifestyle changes, including:
- Consuming a balanced diet with enough calcium and vitamin D
- Engaging in regular weight-bearing exercises
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Maintaining a healthy body weight
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance on reducing the risk of osteoporosis based on your individual needs and medical history.
Should I wear a back brace as osteoporosis treatment?
Wearing a back brace is not typically part of osteoporosis treatment. The focus is on medication, lifestyle changes, and possibly physical therapy to strengthen bones and improve posture. A healthcare provider will recommend the best course of action based on individual needs and symptoms. Remember, early detection and management are key in effectively dealing with osteoporosis.
Final Takeaway
Understanding osteoporosis symptoms is crucial for early detection and management of this condition. By recognizing the common signs and knowing when to seek expert help, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining bone health.
If you experience any concerning osteoporosis symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional promptly is advisable. Remember, knowledge and timely intervention are key to preserving bone density and overall well-being.
Osteoporosis Symptoms Quiz
Test your knowledge about bone health