In the previous years, the Philippines documented several cases of Monkeypox. It began after the pandemic era, in the middle of the year 2022, which lasted in December 2023. Unfortunately, the Mpox spread continues as confirmed cases increased again this August. This month, confirmed cases were raised to 8 active patients, and all are being monitored.
This global outbreak disturbed the peace in every community of the Philippines. Individuals are starting to fear the risk of exposure to the Monkeypox virus, especially due to a lack of knowledge about the conditions. That’s why in this blog, we’ll be focusing on how Mpox spreads by understanding how it can be transmitted. Let’s begin!
Introducing Monkeypox Illness
Before diving into the transmission of this illness, it is important to uncover first the origin of Mpox and how it affected multiple countries around the world.
Monkeypox originated in 1958 when wild animals in parts of Africa like Central and West Africa developed a skin disease that seemed to be chickenpox. It remains unknown how the animals developed this illness. However, they suspect that it might be transmitted from rodents.
In 1970, the first case of Mpox was documented in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Years of research occurred, which allowed the experts to discover that Monkeypox is a zoonotic illness, which can be categorized into 2 clades (e.g., clade I and clade II).
Types of Mpox Virus
As mentioned, there are 2 categories discovered during the thorough research of the experts about Monkeypox. Let’s discuss each of them below!
Clade I
This virus spreads mostly in Central Africa, with 2 subclades known as clade Ia and clade Ib. Clade I is known to be the deadliest variant of Mpox. According to the World Health Organization, this clade is still today’s threat to the Democratic Republic of the Congo. At the end of August 2024, reports from DRC included 4,799 confirmed cases of Mpox, 17,801 suspected cases in DRC, and a total of 610 deaths. All of these cases are identified to be either clade Ia or clade Ib.
However, in 2022, public health emergencies of international concern were raised due to recorded cases in countries like Sweden and Thailand.
Clade II
Meanwhile, as Mpox becomes a global threat, this type of Mpox spreads within African countries and other countries outside Europe. Just like Clade I, it also has subclades (e.g., clade IIa and clade IIb). The global health emergency began in 2022, after the surge of COVID-19.
During that year, cases of clade IIb were documented in countries such as the United States and the Philippines. Recently, another surge of clade IIb was documented in the Philippines with 8 active patients.
While clade II has a lower mortality rate than clade I, it is still important to take precautions, especially when the immune system is at risk. Furthermore, clade II can still lead to symptoms of Mpox, and lead to Mpox spread.
The Impact of Mpox in the Philippines

As of September 2, 2024, news outlets have reported 8 active Mpox cases in the country. That means there’s an ongoing Mpox spread that can affect more Filipinos. In short, this occurrence triggers a risk of infection, which calls for disease control.
Currently, the DOH and other healthcare agencies have been working tirelessly to control the spread of Mpox through supportive care and public awareness initiatives. Despite these efforts, the virus continues to pose a threat, which may involve the lack of constraint, especially when it comes to physical contact.
At the same time, with the lack of protection such as vaccines, situations like continuous Mpox spread are likely to happen. On that note, it is important to seek help from a healthcare provider to address the occurring Mpox symptoms and other threats of Mpox
Documented Details About Mpox Virus in the Philippines
In August this year, DOH uploaded an infographic guide covering crucial details about Mpox, including the symptoms, methods for Mpox spread, and other information.
Common Symptoms of Mpox
Here are the common symptoms people can observe, which can signify the presence of viral infections like Mpox in one’s system.
- fever
- chills
- sore throat and swollen lymph nodes
- muscle aches
- low energy
- rashes
When it comes to Mpox rashes, there are instances where it can occur in a few to several parts of the body. The rashes can progress into Mpox blisters, which can appear on the following body parts:
- palms of the hands
- soles of the feet
- chest
- private part of the body
- groin area
- anal area
Mpox Spread: Common Methods of Transmission
There are different methods on how Mpox spreads. While it may be the same with how chickenpox is transmitted, it is still important to consider that both are highly contagious. Thus, leading to the development of the viral infection through direct contact, airborne, and more.
Let’s discuss each of the known transmission methods below!
Direct Contact with Mpox Spread
Direct contact with an infected individual is one of the modes of Mpox spread. This includes touching the skin lesions or coming into contact with contaminated surfaces. In that case, the sharing of items can be a potential source for Mpox spread.
At the same time, direct contact can also include engaging in sexual activity. Sexual contact involves skin-to-skin contact, which highly transmits the Mpox virus to other people. However, potential Mpox spread can also happen when there are body fluids in contact (e.g., saliva, semen, vaginal fluids, etc.).
Therefore, practicing good hand hygiene and avoiding close contact with infected individuals is essential in preventing the spread of Mpox.
Airborne Transmission of Mpox
In addition to direct contact, Mpox spread through airborne transmission can also happen. Infectious respiratory particles from an infected person can become suspended in the air, which people around can inhale. Thereby, it can contribute to the spread of Mpox. Remember that proper ventilation and wearing masks can minimize the risk of airborne transmission.
Poor Sanitation in Mpox Transmission
Sanitation practices also have a direct impact on Mpox transmission. Proper sanitation measures, such as regular handwashing with soap and water, disinfection of surfaces, and safe waste disposal, can greatly reduce the risk of Mpox transmission. Public education campaigns highlighting the importance of sanitation and hygiene are crucial in preventing the spread of this infectious disease.
By addressing sanitation issues comprehensively, it can make significant strides in controlling Mpox spread and improve the well-being of populations at risk.
Prevention and Control Measures for Mpox
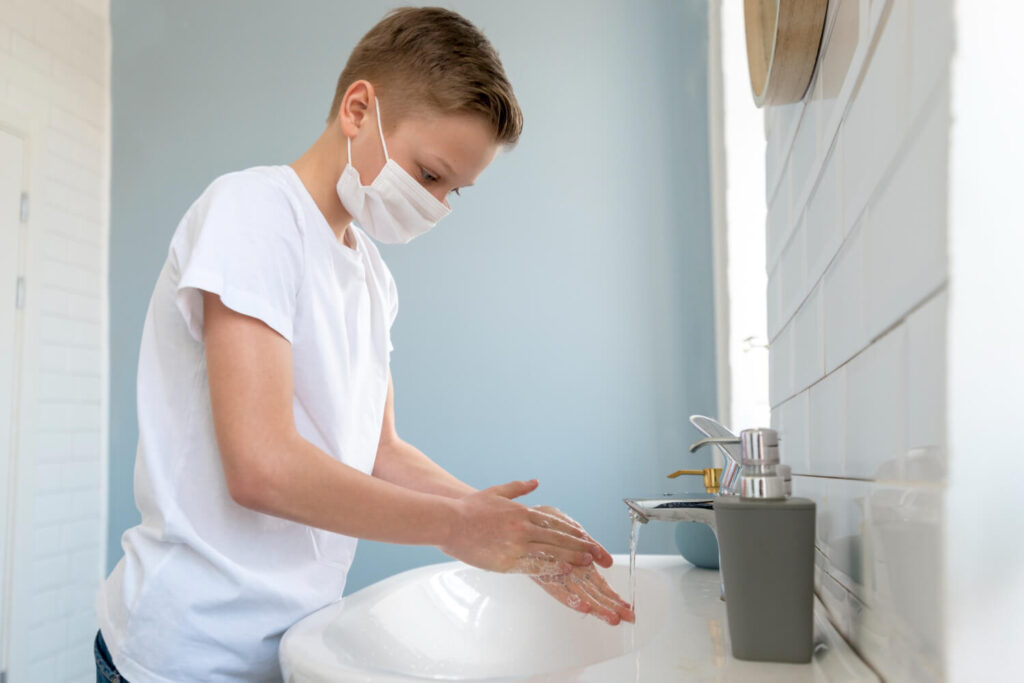

When it comes to prevention of Mpox, a multi-faceted approach is crucial. In the Philippines context, here are some of the feasible actions to use
Personal Hygiene Practices to Prevent Mpox
One of the best options for fighting the Mpox virus is through personal hygiene practices. Regular handwashing with soap and water, covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals are simple yet effective measures that can help prevent Mpox.
Educating the public about the importance of personal hygiene in Mpox prevention is key to fostering behavior change. Community engagement programs that promote hygiene practices and provide access to sanitation facilities can empower individuals to take control of their health and reduce the risk of Mpox transmission.
Eating Healthy Foods to Boost Immune System
Eating a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is essential to boost the immune system and help the body fight off infections like Mpox. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into daily meals can provide the necessary nutrients to support a robust immune system. Additionally, staying hydrated and limiting intake of processed foods and sugars can further aid in maintaining overall health and immunity against Mpox.
Government Response to Mpox
The fight against Mpox requires a collective effort from both the government and the community. Here are some of the current strategies implemented in the Philippines to face the rising cases of Mpox.
Purchasing of 2000 Mpox Vaccines
As of this writing, DOH promises to purchase 2000 Jynneos vaccines to fight off the threat of Mpox in the country. According to the DOH, they’ve requested 2000 doses from the WHO to acquire the vaccine. However, they also stipulated that it would take time to acquire the vaccines, considering the rising number of cases in the DRC.
Offering Free Tests in Governmental Hospitals
Another helpful response to avoid further Mpox spread involves the affirmation of Mpox-free testing in the 2025 budget hearing. According to the Health Secretary of the DOH, people can acquire free testing for Mpox in governmental hospitals. This goal is still in the works, considering the lack of testing supplies. Still, this involvement is an ideal improvement as it can provide access to quality healthcare facilities for better management of one’s health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can asymptomatic patients be a source of Mpox spread?
The role of asymptomatic carriers in Mpox transmission cannot be overlooked. Asymptomatic individuals who are infected with Mpox but do not show any symptoms can unknowingly spread the virus to others. This poses a significant challenge in controlling the spread of Mpox, as identifying and isolating asymptomatic carriers can be difficult. Public health measures such as widespread testing and contact tracing play a crucial role in identifying and isolating symptomatic and asymptomatic cases to prevent further transmission of Mpox.
Is it possible for Mpox to spread through food?
Yes, there’s a chance to spread Mpox through food contamination. Eating animal meat that may have been exposed to such a virus can result in developing Mpox symptoms. However, it can also be prevented by properly cleaning and cooking the meat to ensure safety.
Can pregnant women pass Mpox to their babies?
It is important to note that pregnant women and their babies are likely in danger if they are diagnosed with Mpox. Most cases involve stillbirth, death of the fetus, and other complications that can lead to the death of the baby. In short, health complications can occur, which leads to death rather than the passing of Mpox to a living baby.
Final Takeaway
Monkeypox can be a dangerous illness, depending on the type of virus that people catch. Fortunately, the Philippines was able to catch the less severe case of Mpox, which doesn’t have a high mortality rate. Despite that, a continuous cycle of Mpox spread occurs in the country, which led to the number of active cases today.
In that case, it is important to be vigilant and to stay healthy as needed. If you think that your health has been compromised by the Mpox virus, it’s time to seek help. Book an online consultation with an infectious disease doctor now!
Test Your Mpox Knowledge
5 questions about mpox transmission
Quiz Complete!
Test Your Mpox Knowledge
5 questions about mpox transmission and prevention