A person’s oral health is an important aspect that every individual must prioritize. That’s because there are several conditions that may affect this health aspect, and one of them is horizontal bone loss. This oral condition is a type of bone loss involving the teeth, and even its surrounding structures like gums.
With this kind of threat, it can affect not only the physical structure of one’s gums and teeth, but may also interfere with the overall health of their mouth. That’s because when the gums are affected, it can possibly progress to gingivitis and other gum diseases. Meanwhile, bone loss such as teeth loss can interfere with the person’s speech, eating habits, and other aspects. So, it is important to address it immediately during its earlier stage to prevent these consequences from happening.
Fortunately, this blog can help individuals to understand horizontal bone loss better. Let’s dive deeper into this topic and ensure the long-term health and stability of the teeth and gums.
What is Horizontal Bone Loss?
Horizontal bone loss, also known as alveolar bone loss, is a type of bone loss that occurs in the jawbone. It is characterized by a decrease in the height and density of the alveolar bone, which is the bone that supports the teeth. When the alveolar bone is compromised, it can lead to a loss of support for the teeth, making them more susceptible to mobility and potential tooth loss.
Additionally, horizontal bone loss can affect the surrounding soft tissues, including the periodontal ligament and the gingiva, leading to periodontal disease and other oral health issues. These conditions are characterized by the inflammation and infection of the gums and the subsequent destruction of the supporting structures, including the alveolar bone.
In terms of the severity of the condition, horizontal bone loss can vary, ranging from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the bone loss. Mild bone loss is typically defined as a 1- to 2-mm loss of the supporting bone, while moderate loss is characterized by a loss greater than 2 mm up to half the supporting bone height. Severe horizontal bone loss refers to bone loss beyond this point.
In short, horizontal bone loss is a condition that can have a significant impact on the overall structure and stability of the individual’s teeth. So, it is best to address the condition immediately to reverse its potential threats.
Causes of Horizontal Bone Loss in Patients
Developing horizontal bone loss can happen due to various factors. In most cases, it is primarily caused by periodontal disease, which includes chronic periodontitis, aggressive periodontitis, and others. Periodontal disease is a bacterial infection that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth, including the gums, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone.
Here’s the difference between the 2 diseases that progresses to horizontal bone loss:
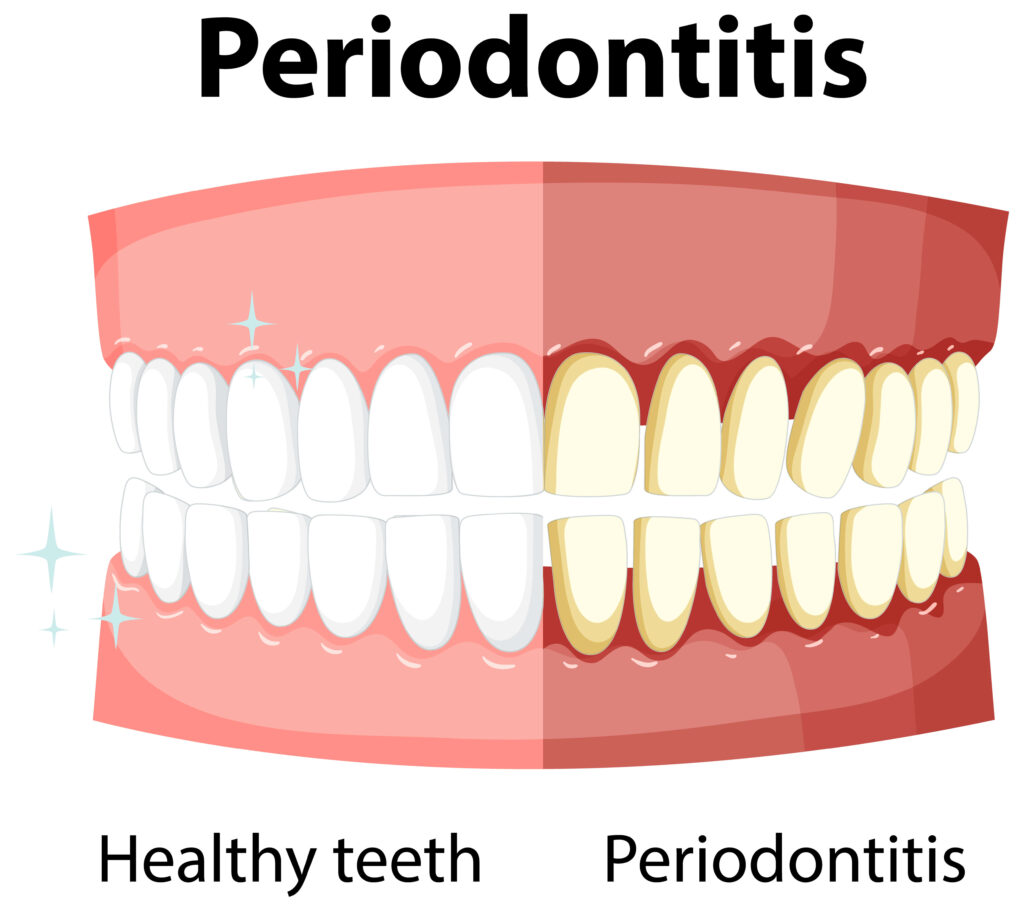
Chronic Periodontitis
It is the more common form of periodontal disease and is characterized by the gradual progression of inflammation and infection in the gums. Over time, the bacteria in dental plaque can cause the gums to recede, forming periodontal pockets. As the infection spreads, it can lead to the destruction of the periodontal ligament and the alveolar bone loss, resulting in horizontal bone loss.
Aggressive Periodontitis
On the other hand, aggressive periodontitis is a more aggressive and rapid form of periodontal disease. It is characterized by severe inflammation and destruction of the periodontal tissues, including the alveolar bone. Thus, also resulting in horizontal bone loss.
Take note that aggressive periodontitis can occur in individuals with a genetic predisposition or can be triggered by certain factors such as hormonal changes or systemic diseases.
Other Contributing Factors
Meanwhile, other factors that can contribute to horizontal bone loss include poor oral hygiene practices, smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, and systemic diseases such as diabetes. These factors can exacerbate the progression of periodontal disease and accelerate the loss of alveolar bone.
It is important for individuals to understand the causes of horizontal bone loss in order to take proactive measures to prevent its progression or seek appropriate treatment. By addressing the underlying periodontal disease and implementing effective oral hygiene practices, individuals can minimize the risk of horizontal bone loss and maintain optimal oral health.
Impact of Horizontal Bone Loss on Oral Health
Effects on Teeth and Gums
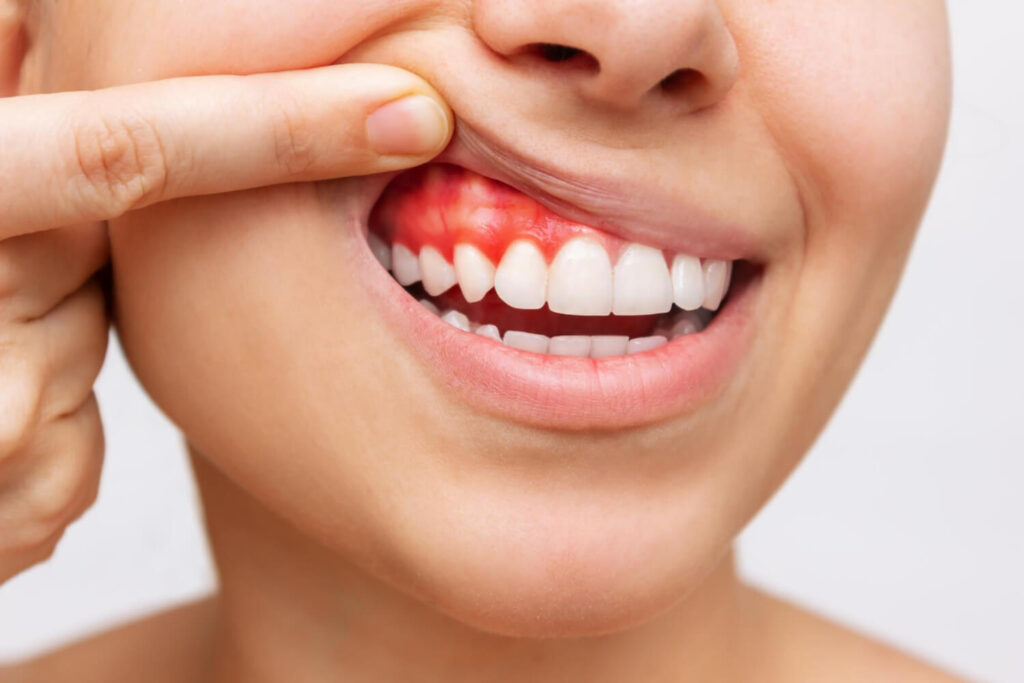
Horizontal bone loss can have significant effects on both the teeth and the gums. As the alveolar bone recedes, the teeth may become more mobile and prone to shifting or even falling out. This can not only affect the function and aesthetics of the smile but also impact overall oral health.
In addition to tooth mobility, horizontal bone loss can also affect the soft tissues surrounding the teeth. The periodontal ligament, which attaches the tooth to the alveolar bone, may become compromised, leading to further instability and potential tooth loss. The gums may also be affected, as the loss of supporting bone can result in gum recession, exposing the sensitive root surfaces of the teeth. This can increase the risk of tooth sensitivity, root decay, and gum disease.
Addressing horizontal bone loss is crucial in order to preserve the stability and health of the teeth and gums. By seeking appropriate treatment and practicing good oral hygiene, individuals can minimize the effects of horizontal bone loss and maintain a healthy smile.
Long-Term Oral Health Risks
Horizontal bone loss can have long-term oral health risks if left untreated. As the alveolar bone recedes, it can lead to attachment loss, where the periodontal ligament detaches from the tooth surface. This can result in the formation of deeper periodontal pockets, making it more difficult to clean and maintain proper oral hygiene. The deeper pockets can harbor bacteria and plaque, increasing the risk of gum disease and other oral infections.
Furthermore, horizontal bone loss can also impact the overall structure and alignment of the teeth. As the supporting bone diminishes, the teeth may shift or become misaligned, potentially leading to bite problems and difficulties with chewing and speaking.
It is important to address horizontal bone loss as early as possible to minimize the long-term oral health risks. Seeking appropriate treatment from a periodontist and maintaining good oral hygiene practices can help prevent further bone loss and preserve the health and stability of the teeth and gums.
Identifying Signs of Horizontal Bone Loss
While horizontal bone loss may not be visible to the naked eye, there are several signs and symptoms that may indicate its presence. One of the key indicators of this type of bone loss is tooth mobility or a change in the alignment of the teeth. As the supporting bone diminishes, the teeth may become loose or shift out of their normal position. This can be particularly noticeable when biting or chewing.
Another indication of this condition is the presence of deep periodontal pockets. These pockets form when the gums recede and detach from the tooth surface, exposing the underlying bone. Periodontal probing can be used to measure the depth of the periodontal pockets and assess the extent of the bone loss.
It is important to consult a periodontist if any of these signs or symptoms are present. A periodontist is a dental specialist who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of periodontal diseases, including horizontal bone loss. They have the expertise and tools necessary to properly assess the condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
When to Consult a Periodontist

If you suspect that you may have horizontal bone loss or are experiencing any signs or symptoms of periodontal disease, it is important to consult a periodontist. A periodontist is a dental specialist who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of periodontal diseases, including this condition.
Periodontists have advanced training and expertise in the field of periodontics, which focuses on the supporting structures of the teeth, including the gums and alveolar bone. They are skilled in the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of periodontal diseases, and can provide the necessary care and guidance to address horizontal bone loss.
When you visit a periodontist, they will conduct a comprehensive examination of your oral health, including a thorough evaluation of your gums and supporting structures. They may also take radiographs and perform other diagnostic tests for thorough assessment.
In short, by consulting a periodontist, you can ensure that you receive the highest quality care and achieve the best possible outcomes for your oral health.
Strategies for Reversing Horizontal Bone Loss

Reversing horizontal bone loss is a complex process that requires a multi-faceted approach. The strategies for reversing it may include both non-surgical treatment options and surgical interventions, depending on the severity of the bone loss.
Consulting with a periodontist will help determine the most appropriate strategies for reversing the effects of the condition and restore optimal oral health. Let’s discuss the non-surgical and surgical approach that the periodontist may recommend.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatment options for reversing horizontal bone loss focus on stimulating the body’s natural regenerative abilities to promote the growth of new bone and soft tissue. These treatment modalities can be highly effective in addressing bone loss and restoring oral health.
Some non-surgical treatment options include:
- Stem cell therapy: Stem cells have the potential to differentiate into various types of cells, including bone cells. By harnessing the regenerative capabilities of stem cells, they can be used to promote the growth of new bone and tissue in the affected area.
- Regenerative therapy: This approach involves the use of growth factors and other biologically active substances to stimulate the regeneration of lost bone and tissue. It can help promote the growth of new blood vessels and bone cells, ultimately reversing the effects of the condition.
These non-surgical treatment options can be highly effective in addressing horizontal bone loss, particularly in less severe cases. However, it is important to consult with a periodontist to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for your specific needs.
Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases
In more severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to restore the lost bone and supporting structures. These surgical techniques aim to rebuild the damaged bone and promote the regeneration of healthy tissues. Some common surgical interventions include:
- Bone grafting: This procedure involves the transplantation of bone from another part of the body or the use of synthetic materials to rebuild the lost bone. The bone graft serves as a scaffold for the growth of new bone and helps restore the integrity and stability of the jawbone.
- Tissue engineering: This approach involves the use of biocompatible materials and growth factors to promote tissue regeneration. Tissue engineering techniques can also help stimulate the growth of new bone and soft tissue. Thus, ultimately reversing the effects of horizontal bone loss.
These surgical interventions can be highly effective in restoring the lost bone and supporting structures in severe cases of this type of bone loss. It is important to consult with a periodontist to determine the most appropriate surgical technique for your specific needs.
Preventive Measures Against Horizontal Bone Loss

While treatment options are available for addressing this oral health condition, prevention is always better than cure. Taking proactive measures to prevent horizontal bone loss can help maintain optimal oral health and minimize the risk of developing periodontal disease.
Some preventive measures may include:
Daily Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for preventing periodontal disease and horizontal bone loss. Proper daily oral hygiene practices can help remove plaque, prevent the buildup of tartar, and keep your teeth and gums healthy. Some key daily oral hygiene practices include:
- Brushing your teeth: Brush your teeth twice a day for two minutes each time using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Make sure to brush all surfaces of your teeth, including the front, back, and chewing surfaces.
- Flossing: Floss your teeth at least once a day to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline. Use a gentle sawing motion and be sure to reach all the way down to the gumline.
- Using mouthwash: Rinse your mouth with an antimicrobial mouthwash after brushing and flossing to help kill bacteria and freshen your breath.
- Tongue cleaning: Use a tongue scraper or your toothbrush to gently clean your tongue, as bacteria can accumulate on its surface.
By incorporating these daily oral hygiene practices into your routine, you can maintain optimal oral health and minimize the risk developing the oral condition.
Regular Dental Check-Ups and Cleanings
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are essential for maintaining good oral health and preventing periodontal diseases. During these visits, your dentist will thoroughly examine your teeth and gums, looking for any signs of horizontal bone loss or other oral health issues. They may also perform a professional cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup that cannot be removed through regular brushing and flossing.
It is recommended to visit your dentist at least twice a year for routine check-ups and cleanings. However, the frequency of your visits may vary depending on your individual needs and oral health condition. Your dentist will be able to provide guidance on the appropriate schedule for your check-ups and cleanings.
By staying proactive with your dental check-ups and cleanings, you can catch any potential issues early on and take the necessary steps to prevent further damage and maintain optimal oral health.
Conclusion
Horizontal bone loss can significantly impact oral health, leading to potential risks if left untreated. By taking proactive steps, you can reverse such type of bone loss and safeguard your oral health for the long term. That involves the different preventive measures provided by the doctor.
If you are planning on reversing the effect of horizontal bone loss, it is important to seek immediate help. Book an online consultation with a periodontics doctor today!
Horizontal Bone Loss Quiz
Test your knowledge about alveolar bone loss and oral health