When it comes to liver conditions, one of the life-threatening illnesses is hepatitis. It is considered a silent killer due to patients not recognizing they have the condition until it’s too late. Due to its nature, patients need to understand this illness thoroughly to combat its effect on the liver before it results in dysfunction. The best way to begin is through knowing the common hepatitis symptoms.
If you think you are a possible hepatitis patient, this blog is for you. Learn more about these liver disease symptoms and how they can result in liver failure. Let’s begin!
Understanding Hepatitis
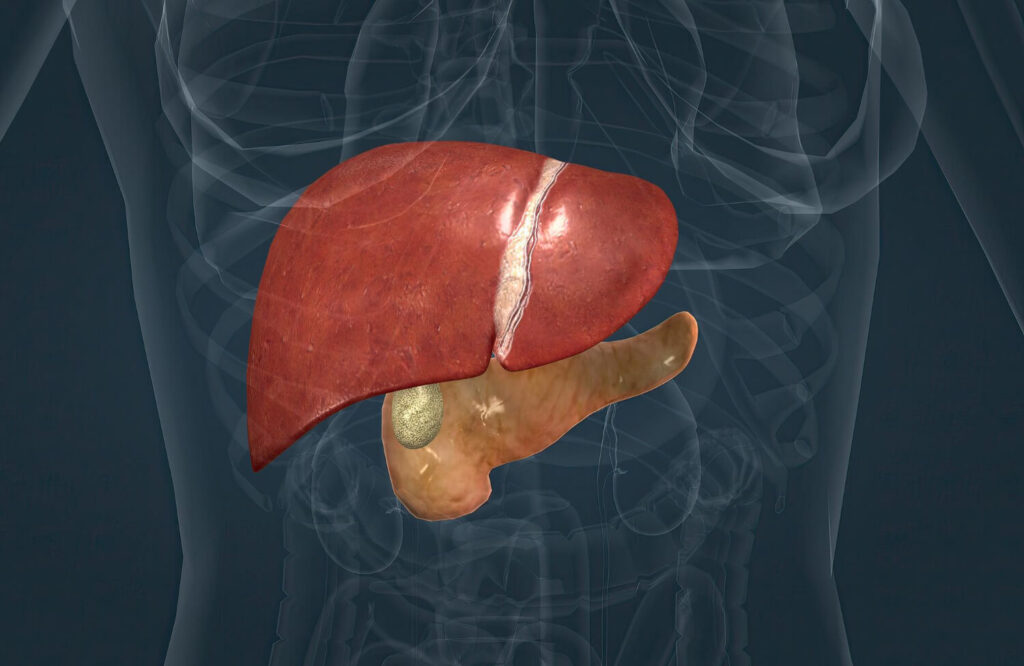
Inflammation in the liver is commonly associated with hepatitis. That happens due to an infection that targets the liver cells. This infection causes inflammation and potentially leads to serious health complications.
Unfortunately, with a compromised liver, its function is also affected. It is important to note that the liver is responsible for detoxifying the body, producing bile, and storing essential nutrients. Without these functions, the body becomes weaker, especially the immune system. Thus, resulting in a wide range of symptoms and complications.
In the case of hepatitis symptoms, there are cases wherein mild symptoms can occur. These hepatitis symptoms can resolve on their own, which is one of the ideal cases for patients. However, some can experience progression of symptoms, which means they can suffer from severe complications. That’s why there are asymptomatic patients who experience severe conditions due to the silent killing effect of the condition. Some instances result in liver damage because of no visible symptoms.
Different Types of Hepatitis
There are several types of hepatitis, each with its causes and characteristics. These types are known to have different transmission methods to individuals but, still harbor the effect of liver damage when not properly assessed and treated early on.
Here are the common types of hepatitis
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is usually transmitted through contaminated food or water. The hepatitis A virus or HAV is found in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene practices. That’s why it is encouraged to be alert to what you eat and drink, especially when eating out.
Hepatitis B
On the other hand, hepatitis B involves the transmission of the hepatitis B virus or HBV through contact with infected blood or other body fluids. This type of hepatitis can be spread through sexual contact or from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth. It is important to note that Hepatitis B can both result in acute and chronic infection and lead to severe liver damage if left untreated.
Hepatitis C
Moving on to hepatitis C, the hepatitis C virus or HCV is primarily transmitted through blood-to-blood contact. This type of hepatitis can occur through sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia, as well as receiving a blood transfusion from an infected donor before proper screening procedures are implemented. It can also be transmitted through sexual contact, although this is less common.
Hepatitis D
Meanwhile, hepatitis D, also known as delta hepatitis, is a unique type of viral infection that can only occur in individuals who are already infected with hepatitis B. It is considered a superinfection because it requires the presence of Hepatitis B to replicate and cause damage to the liver.
Hepatitis E
Lastly, hepatitis E, this type of viral infection is primarily transmitted through contaminated water and food. It is most commonly found in areas with poor sanitation and limited access to clean drinking water. Unlike Hepatitis B and C, Hepatitis E does not typically cause chronic liver disease or other long-term complications.
It is important to note that hepatitis can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or socioeconomic status. By understanding the different types of hepatitis, their causes, and potential complications, inflammation of the liver can be addressed, ensuring a healthier and functional liver.
Common Hepatitis Symptoms
Physical Signs of Hepatitis

Many individuals with hepatitis experience physical symptoms that indicate liver inflammation. These may include the following:
- fatigue
- jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- dark urine
- pale stools
- abdominal pain
- tenderness in the liver area
It is a must to be observant when it comes to their occurrence. Doing so allows you to confirm whether or not you have contracted the condition, especially if there are outbreaks in the area. Acknowledging these signs, and their occurrence signals the time for proper diagnosis. In short, these signs signify the need to schedule an appointment with a hepatologist.
Changes in Body Functions

Aside from the physical signs, there are also additional hepatitis symptoms that can verify the occurrence of viral hepatitis in your liver. These signs include changes in your normal body functions. Let’s dwell on them below!
- Loss of appetite: a common symptom as the inflammation in the liver can affect the body’s ability to digest and absorb nutrients properly.
- Nausea and vomiting: Occur as a result of the liver’s reduced ability to process toxins, leading to a buildup of waste products in the bloodstream.
- Weight loss: The change experienced by individuals with hepatitis is weight loss. The inflammation results in the combination of loss of appetite and the body’s increased metabolic demands, leading to a decrease in body weight.
- Fever: As a result of the infection, the normal body temperature and immune system changes, leading to a fever.
Symptoms Specific to Certain Types of Hepatitis
Each type of hepatitis may also present its specific symptoms. For example, hepatitis B and C can lead to chronic infections, which may cause long-term liver damage, while hepatitis A often resolves on its own without causing chronic infection. Let’s discuss each of them fully:
Hepatitis A
The hepatitis symptoms that commonly occur for this type include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. However, unlike hepatitis B and C, hepatitis A does not typically lead to long-term liver damage. This type is known for its acute infection and can resolve on its own without causing chronic infection.
Hepatitis B and C
Hepatitis B and C are known for their ability to cause chronic infections, meaning the virus can remain in the body for an extended period. This can lead to ongoing liver inflammation and damage, potentially resulting in cirrhosis or liver cancer if left untreated. Common symptoms of chronic hepatitis B and C include fatigue, abdominal pain, and jaundice.
Hepatitis D
Meanwhile, the hepatitis symptoms of hepatitis D may include immune system changes, fatigue, abdominal pain, and jaundice. Hepatitis D is unique in that it can only occur in individuals with hepatitis B. This means that the symptoms of hepatitis D may overlap with those of hepatitis B. However, the combination of both viruses can result in more severe liver damage than either virus alone.
Hepatitis E
On the other hand, this type of hepatitis can affect adults, specifically 50 years and up. They may experience the following hepatitis symptoms such as fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and yellowing of the skin and eyes.
It is important to note that while these symptoms are often associated with their respective types of hepatitis, individual experiences may vary. Some individuals may exhibit additional symptoms or may not experience certain symptoms at all. If you suspect you may have hepatitis or are experiencing any concerning symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Why Early Intervention is Important
Prompt diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further liver damage and complications. With the prominent risk of compromised liver function, it is best to seek early interventions as early as possible.
For instance, chronic hepatitis can have serious long-term consequences, including liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. By seeking medical attention early on, individuals with hepatitis B or C can be monitored closely and receive appropriate treatment to manage the infection and minimize the risk of complications.
Additionally, for those diagnosed with acute hepatitis A, early intervention can help alleviate symptoms and support the body in recovering more quickly. While hepatitis A often resolves on its own, seeking medical care can ensure that any discomfort or complications are addressed promptly.
Another reason why early intervention is crucial is because hepatitis is highly contagious. In the case of hepatitis A, the virus spreads through contaminated food or water, while hepatitis B and C can be transmitted through unprotected sexual contact, sharing needles, or exposure to infected blood.
By diagnosing and treating hepatitis early, individuals can take steps to prevent further transmission of the virus to others. Thus, ensuring a healthier community by preventing the virus widespread. So, if you are suffering from a series of symptoms, it’s best to seek immediate help. Explore the online consultation options by visiting your local hospitals for a health check-up.
Undergoing Medical Procedure for Hepatitis Diagnosis
Once you decide to visit a healthcare expert for an accurate diagnosis and disease control, the doctor may require test procedures to identify your current condition. These procedures can be invasive and non-invasive tests, which can help them assess your liver health.
Invasive tests, such as a liver biopsy, will occur to obtain a small sample of liver tissue for further analysis. This procedure involves inserting a needle into the liver to extract the sample, which experts examine under a microscope to check for any signs of inflammation or damage.
Meanwhile, non-invasive tests provide valuable information about your liver without a surgical procedure. These tests include blood tests that measure specific enzymes and antibodies associated with hepatitis, as well as imaging techniques like ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
Depending on your symptoms and medical history, your doctor may recommend a combination of invasive and non-invasive tests to diagnose your condition accurately.
Treatment Options for Hepatitis Patients
Once a diagnosis of hepatitis is confirmed, there are several treatment options available for patients. The choice of treatment depends on the type and severity of hepatitis, as well as the individual’s overall health. Let’s discuss the possible treatment plan for the different types of hepatitis.
Hepatitis A
For the infected person due to hepatitis A, they can utilize medications such as antiviral drugs to help treat the symptoms and alleviate discomfort. However, in most cases, hepatitis A does not require specific treatment as it tends to resolve on its own over time. The main focus of treatment is to manage symptoms such as fatigue, nausea, and jaundice through rest, a healthy diet, and proper hydration.
Hepatitis B
Treatment for hepatitis B may involve antiviral medications that can help slow down the replication of the virus in the liver and reduce the risk of complications. Regular monitoring of liver function and viral load is vital to assess the effectiveness of treatment and adjust medication dosage if needed.
Hepatitis C
Meanwhile, advancements in medical research have led to the development of highly effective antiviral medications for treating hepatitis C. These direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) can cure the infection in most cases. Treatment duration can vary based on the specific genotype of the hepatitis C virus and the individual’s overall health. Typically, treatment can range from 8 to 12 weeks but can extended in some cases. It is important to note that early detection and prompt treatment of hepatitis C can significantly improve outcomes and prevent long-term complications such as liver cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Hepatitis D
Unfortunately, there are limited treatment options available for hepatitis D. The primary approach involves managing symptoms and providing supportive care to prevent further liver damage. In some cases, doctors will prescribe antiviral medications to help suppress the replication of the hepatitis D virus. However, these medications are not always effective and may not lead to a complete cure. Therefore, individuals with hepatitis D must receive regular monitoring and follow-up care to manage their symptoms and prevent complications.
Hepatitis E
Similar to hepatitis A, most cases of hepatitis E do not require specific treatment as they tend to resolve on their own with time. The focus is primarily on managing symptoms such as fatigue, fever, and abdominal pain through rest and supportive care. However, pregnant women with hepatitis E should seek medical attention as the infection can be more severe and pose risks to both the mother and the unborn baby.
Final Takeaway
Detecting hepatitis symptoms and seeking timely medical attention is essential for managing this potentially serious condition. By understanding the types of hepatitis and recognizing the hepatitis symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps toward early detection and effective treatment.
Remember, ignoring the signs of hepatitis can have long-term consequences on liver health, so it is essential to prioritize your well-being. Consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns. Book an online consultation or visit a hepatologist near you.
Hepatitis Awareness Quiz
Test your knowledge about hepatitis symptoms and prevention
Great Job!
You have a good understanding of hepatitis.