Another form of viral hepatitis involves the patient being at risk due to exposure from infected blood. It commonly occurs when a person is infected with contaminated blood, leading to hepatitis C. There are still other instances that can lead to being infected, but how can you confirm its occurrence?
In this blog, we’ll cover the common signs of hepatitis c, the health problems it can bring to patients, and the suitable health care treatment for a better liver health. Let’s begin!
The Prevalence of Hepatitis C Worldwide
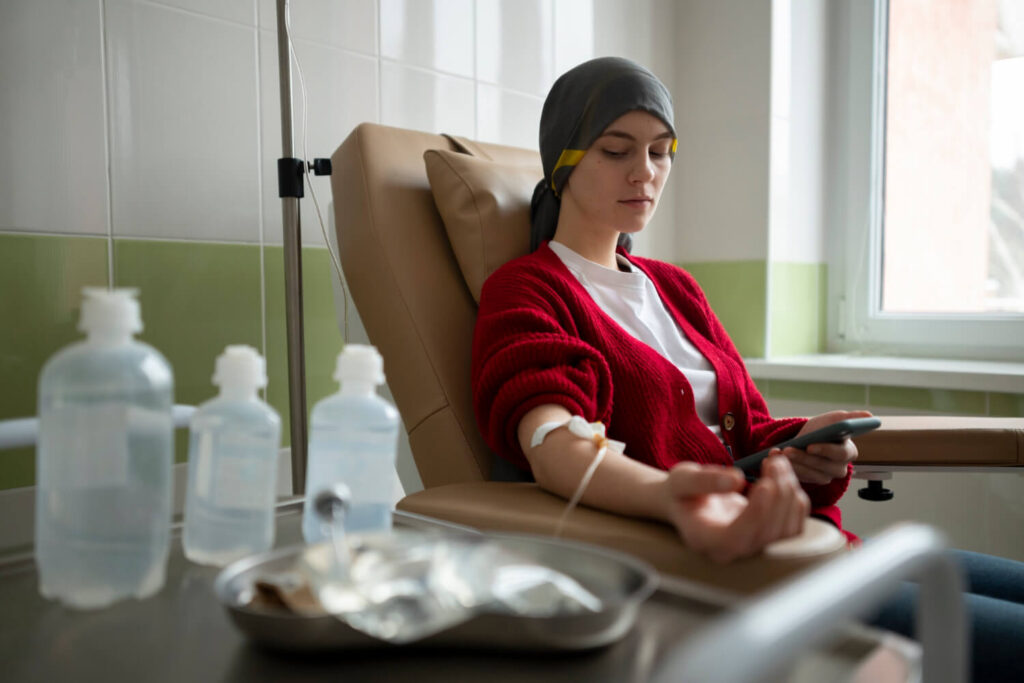
When it comes to understanding hepatitis c, it is best to discuss why it has been a prevalent condition that involves the blood. That’s because, when this virus enters the body, it targets liver cells and begins to replicate. This can lead to inflammation and damage to the liver over time.
Hepatitis C is a contagious liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus. It is primarily transmitted through contact with infected blood, such as sharing needles or equipment for injecting drugs, receiving unscreened blood transfusions or organ transplants, or coming into contact with blood from an infected person through accidental pricks or cuts.
While some individuals may experience only acute infection and recover within a few months, most people develop a chronic infection that can last a lifetime. Chronic hepatitis C is a major cause of liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, and liver failure.
It is a global health concern, with an estimated 71 million people living with chronic HCV infection worldwide. However, it is important to note that hepatitis C can affect individuals from all walks of life, regardless of their geographic location. This potential threat is being monitored by the World Health Organization to help combat the rising number of infected people.
Hepatitis A vs Hepatitis B vs Hepatitis C
Considering hepatitis is a rampant condition, of course, there are other variants of this inflammation in the liver. Currently, there are 5, but let’s focus first on the 3 common types.
Hepatitis A
This first type of hepatitis is caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV). Unlike hepatitis C, which is primarily transmitted through blood contact, hepatitis A is mainly spread through contaminated food or water. It is commonly found in areas with poor sanitation and inadequate hygiene practices.
The symptoms of hepatitis A typically include fatigue, nausea, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, and jaundice. However, unlike hepatitis C, most cases of hepatitis A resolve on their own without causing long-term liver damage. Vaccines are available to prevent hepatitis A infection, making it a preventable disease.
Hepatitis B
Meanwhile, hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Similar to hepatitis C, HBV is primarily transmitted through contact with infected blood or other body fluids. This can occur through sexual contact, sharing needles or syringes, or from mother to child during childbirth.
Its main difference from hepatitis C is how the blood transmission works. For hepatitis B, it is common to be transmitted only through childbirth, from mother to their baby. Meanwhile, hepatitis C involves injection.
The Silent Progression: Hepatitis C Symptoms
Early Stage Symptoms of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that results in the inflammation of the liver due to the virus. It is often referred to as a silent disease because many individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms during the early stages of hepatitis c virus infection. This silent progression makes it challenging to diagnose the condition in its initial phases.
However, as the infection progresses, some people may begin to experience symptoms. These early stage symptoms of hepatitis C can include fatigue, muscle and joint pain, fever, and loss of appetite. While these symptoms may seem mild and easily dismissible, it is important to take note of them as they could be indicative of hepatitis C.
That’s why with these warning signs, it is a must to take action and visit a health professional. Doing so allows you to take early intervention before it results in serious liver damage.
Chronic Hepatitis C Symptoms
Unfortunately, if the patient still disregards the condition despite the multiple early warning signs, it can result in chronic hepatitis C. It is known to provide life-threatening complications to the patients. Although, It is important to note that not everyone with chronic hepatitis C will experience symptoms, and some individuals may remain asymptomatic for years.
Let’s discuss some of the common symptoms for this chronic illness:
Fatigue
For those who do experience symptoms, ongoing fatigue is a common complaint. This fatigue can persist for extended periods and can significantly impact daily life. Individuals may find it difficult to maintain their usual level of activity and may need to rest frequently.
Jaundice
Meanwhile, this condition is characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes. This yellow discoloration is a result of the liver’s inability to properly process bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced when red blood cells break down. Jaundice can be a sign of liver damage and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Nausea and Abdominal Pain
In addition to fatigue and jaundice, individuals with chronic hepatitis C may experience abdominal pain. This pain can range from a dull ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation. It is often located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen and can be accompanied by bloating and discomfort. Furthermore, nausea occurs making it difficult for individuals to eat and can contribute to weight loss and malnutrition.
Dark Urine
On the other hand, another symptom that individuals with chronic hepatitis C may experience is dark urine. The urine may appear darker in color than usual, ranging from amber to brown. This change in urine color is a result of the liver’s impaired ability to eliminate waste products from the body.
It is worth noting that these symptoms can also be associated with other health conditions, such as UTI. Thus, underscoring the need for accurate clinical diagnosis. If you suspect you may have hepatitis C or are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a hepatologist for proper evaluation and testing.
The Importance of Early Detection

When it comes to liver health, early detection is a must to avoid serious health problems. With a compromised liver, it can affect its normal functions, resulting in other health complications. In short, your immune system can also be affected with the increased HCV infection. The worst case scenario is undergoing liver transplantation due to liver damage caused by the untreated condition.
So, if you are currently experiencing the discussed symptoms above, you can receive the suitable treatment options through seeking an expert’s help.
The Role of Testing in Hepatitis C Management
Testing plays a crucial role in the management of hepatitis C. It does not only diagnose the infection but also provides valuable information for monitoring the progress of treatment. Regular testing during and after treatment can determine the effectiveness of antiviral medications and whether the virus has been cleared from the body.
In addition to blood tests, other diagnostic tools such as liver function tests and imaging studies may be used to assess the extent of liver damage caused by hepatitis C. These tests help healthcare providers evaluate the overall health of the liver and determine the appropriate course of action.
Furthermore, testing is not only important for individuals with known risk factors but also for the general population. Many people with hepatitis C are unaware of their infection because the virus often does not cause noticeable symptoms until the liver damage is severe. Therefore, widespread testing can help identify individuals who may be unknowingly living with hepatitis C and provide them with the necessary care and treatment.
When to Get Tested for Hepatitis C
Risk Factors that Necessitate Testing
There are certain conditions that can help you identify whether or not you should proceed with the tests for hepatitis C. These scenarios can range from self- inflicted to exposure from others. If you have engaged in activities that put you at risk for hepatitis C, it is crucial to get tested.
High-risk behaviors include the following:
- injecting drugs with shared needles or paraphernalia
- receiving blood transfusions or organ transplants before 1992
- having a sexual partner with hepatitis C
- born to a mother with hepatitis C
- healthcare workers who have been exposed to HCV-infected blood
What to Expect During the Testing Process
Types of Hepatitis C Tests
There are different types of tests used to diagnose hepatitis C. The most commonly used test is the antibody test, which detects the presence of HCV antibodies in the blood. If the antibody test is positive, confirmatory tests, such as nucleic acid tests (NAT) or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, are used to determine the viral load and genotype of the infection.
Interpreting Your Test Results
A positive test result indicates an active hepatitis C infection. However, it does not indicate the severity of the infection or the extent of liver damage. Additional tests may be necessary to determine the appropriate treatment approach. Meanwhile, a negative test result means that no HCV antibodies were detected in the blood. However, it is important to note that a negative result does not necessarily rule out a recent infection. If there is a strong suspicion of recent exposure to hepatitis C, further testing may be required.
In both cases, the interpretation of the test results must be fully explained by the hepatologist. This health expert has expertise regarding this condition, especially the points on how to resolve the current illness. It’s best to communicate all of your questions and concerns to have a middle ground on how to approach the condition.
That is important, especially if you have an existing health condition that may be of conflict with the possible medications. Don’t worry as you are entitled to receive a quality care service from the doctor as your health is their top priority.
Treatment for Hepatitis C
Treatment for Hepatitis C typically involves a combination of antiviral medications. The goal of treatment is to eliminate the virus from the body and prevent further liver damage. The specific medication regimen will depend on various factors such as the genotype of the virus and the extent of liver damage.
Furthermore, new antiviral drugs have revolutionized the treatment landscape for Hepatitis C. It offers higher cure rates with fewer side effects. These direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) work by targeting specific steps in the HCV replication cycle, effectively stopping the virus from multiplying.
The duration of treatment can vary depending on the current condition of your infection. In that case, it is possible your treatment plan is different from what the others have. So, it is still ideal for you to schedule an appointment with a health expert. That way the doctor can specifically create a tailored treatment plan suitable for you.
Conclusion
One of the serious liver infection conditions is hepatitis C. Patients suffering from this condition often don’t recognize they have it. That’s why understanding the possible hepatitis C symptoms are vital for their health. Through acknowledgment of the symptoms through early detection, they can address the illness immediately. Thus, preventing life-threatening illnesses from occurring due to liver failure.
If you are one of the patients that suffer from potential hepatitis C virus, this blog is your signal to prioritize your health. Don’t forget to monitor your condition to verify whether or not there’s an ongoing infection and inflammation. If that’s the case, seek help from your local hepatologist.
Book an online consultation or visit your local health centers to address your condition today!
Hepatitis C Knowledge Quiz
Test your understanding of Hepatitis C symptoms, transmission, and treatment
Quiz Complete!
Great job testing your knowledge about Hepatitis C!
Concerned About Hepatitis C?
Get tested and consult with a specialist. Early detection leads to better outcomes with modern treatments offering high cure rates.



