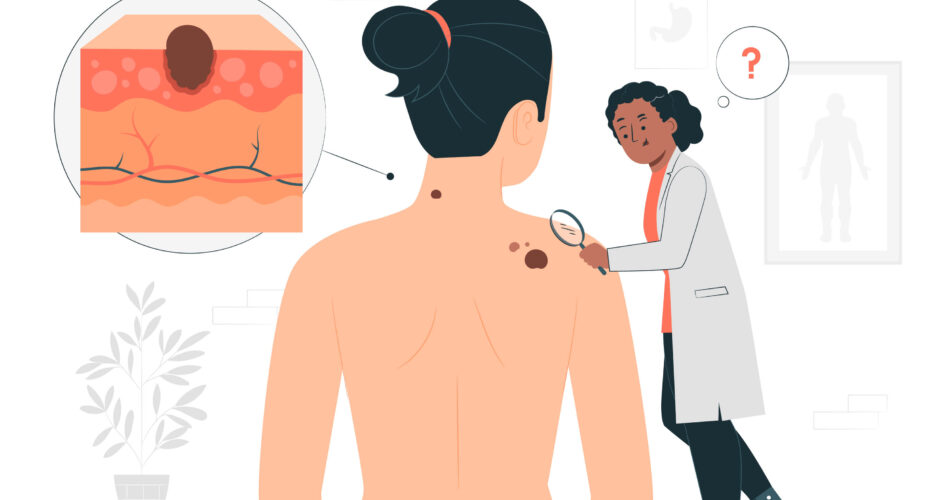
When it comes to dealing with melanoma, patients must be ready for the possible health risks that may come. That’s because melanoma is a skin cancer known for its invasive nature. In short, it is considered the most dangerous skin cancer a patient can develop. Despite that, this type of skin cancer can still be treated, which is why early intervention is a must. With proper guidance, individuals who suffer from this condition can have a chance to manage their skin health better.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the crucial aspects of melanoma. Discover what causes this condition to develop, the signs that indicate its presence, and the effective strategies to manage it. So, whether or not you have melanoma, this comprehensive guide can help. Let’s begin!
What is Melanoma?
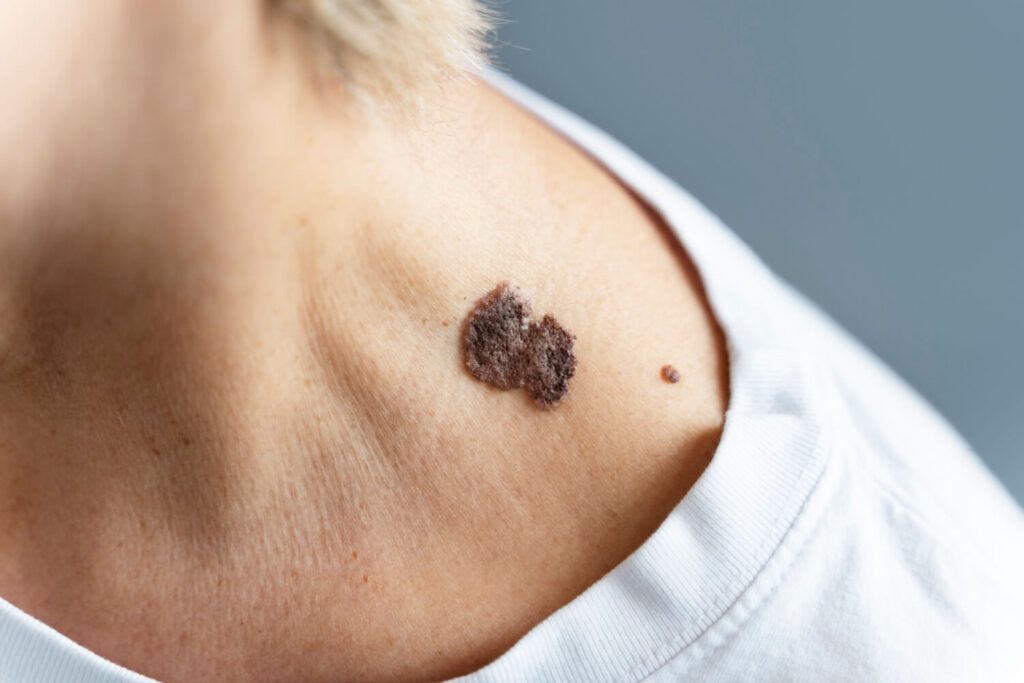
Melanoma or malignant melanoma is a malignant tumor that originates in the skin cells called melanocytes. These cells produce melanin, the pigment that gives our skin its color. In the case of melanoma, there’s an abnormal growth of melanocytes. Unlike normal skin cells, these melanocytes become cancerous and can invade nearby tissues or spread to distant parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
When melanoma develops, it often appears as a new spot or a change in an existing mole. It can vary in appearance, from a small, dark, irregular spot to a large, multicolored lesion with uneven borders. Furthermore, melanoma can also develop in other parts of the body, such as the scalp, eyes, soles of the feet, nail bed, palms of the hands, etc. Early detection and treatment are crucial in improving the prognosis of melanoma.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Melanoma
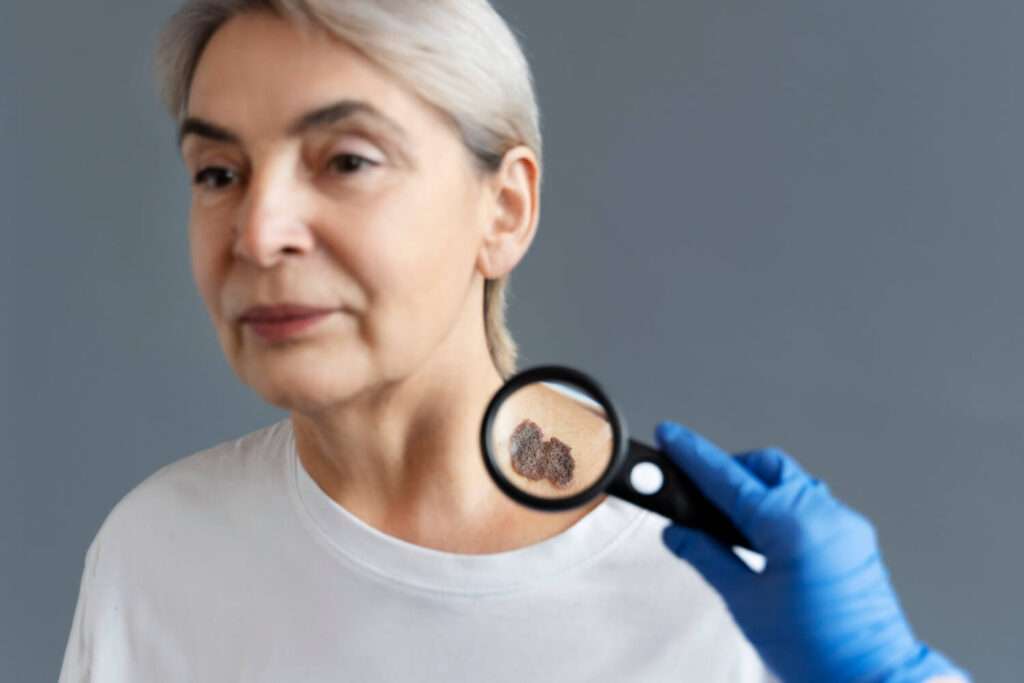
As mentioned, early detection is for successful treatment. In that case, being aware of the common signs of skin cancer like melanoma can help in identifying the disease at an early stage.
Physical Indications
Regular self-examinations of the skin can help spot any new or evolving growths that may indicate melanoma. One of the primary signs of melanoma is the appearance of a new spot or growth on the skin. These spots may have irregular shapes, have uneven borders, or exhibit various colors, including shades of brown, black, blue, red, or white.
Another indication of melanoma is the alteration in the appearance of existing moles such as unusual skin changes or growth at the surrounding skin. Any change in size, shape, color, or texture, as well as bleeding, itching, or crusting, should be carefully evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Take note that individuals with many moles or a history of sunburns are at an increased risk of developing melanoma. Individuals in these high-risk categories must be vigilant about changes in their moles and seek medical attention promptly.
Uncovering the Causes of Melanoma
The exact cause of melanoma is not yet fully understood. However, several risk factors have been identified that may increase the likelihood of developing this type of skin cancer.
Let’s discuss them below!
Genetic Factors
Studies have shown that genetic mutations can predispose individuals to melanoma. People with a family history of melanoma or those who carry specific genetic mutations, such as the BRAF or CDKN2A gene mutations, may have an increased risk of developing the disease.
Environmental Triggers
Meanwhile, exposure to ultraviolet radiation, or UV light from the sun and tanning beds, is a significant environmental risk factor for melanoma. Both emit UVA and UVB, which are associated with skin cancer development. The radiation damages the DNA within skin cells. Over time, this DNA damage can lead to mutations that cause the cells to grow and divide uncontrollably, eventually resulting in melanoma.
Diagnosing Melanoma
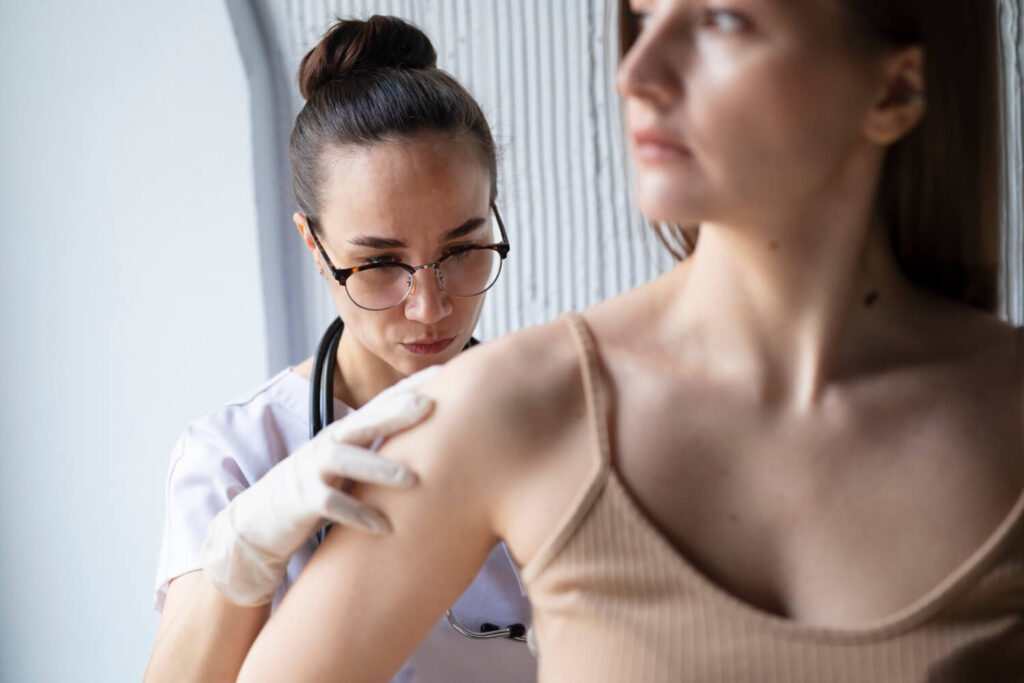
When diagnosing melanoma, healthcare professionals employ techniques and procedures to ensure comprehensive skin assessment. This meticulous approach is essential in catching any suspicious lesions or signs of melanoma at its earliest stages. If the condition is evident, the doctor will then refer to the test results to create effective treatment options.
Here are the diagnostic tools that doctors may recommend for patients:
Skin Examinations
During a skin examination, a healthcare professional will carefully examine the skin for skin cancer signs like suspicious lesions or changes in existing moles. This assessment may involve dermatoscopes, specialized devices that allow a closer examination of skin structures.
Furthermore, skin examinations are not limited to just visual inspections. Dermatologists may also utilize advanced imaging technologies such as reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) to obtain high-resolution images of skin layers, aiding in the early detection of melanoma.
Biopsy Procedures
If a suspicious lesion is identified, a biopsy will be performed to confirm the diagnosis of melanoma. There are different types of biopsies, including excisional, incisional, and punch biopsies, which are used depending on the size and location of the lesion.
Moreover, in addition to traditional biopsy methods, molecular testing techniques like fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and gene expression profiling are increasingly being utilized to provide more detailed information about the genetic characteristics of melanoma cells, aiding in personalized treatment approaches.
Staging and Severity Assessment
Once melanoma is diagnosed, further tests may be conducted to determine the stage and severity of the disease. Staging helps determine the extent of cancer spread and guides treatment decisions.
Additionally, advancements in imaging technologies such as positron emission tomography (PET) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) play a crucial role in accurately staging melanoma. These tools can provide detailed information about the size and location of tumors and their potential spread to lymph nodes or other organs.
Treatment Options for Melanoma
After assessing the patient’s skin health, the doctor must formulate a treatment plan. There are several effective approaches to managing melanoma. Let’s get to know them and how they can help patients with melanoma.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is often the primary treatment for localized melanoma. It may involve removing solid tumors and a margin of healthy tissue surrounding them. In cases of advanced melanoma, surgery may be combined with other treatments.
Radiation Therapy
Meanwhile, radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. Aside from melanoma, other types of skin cancer can also be managed using this option. It may be used after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells in the area or as a palliative treatment to relieve symptoms in advanced cases.
Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy
On the other hand, immunotherapy and targeted therapy have revolutionized the treatment of advanced melanoma. These therapies work by stimulating the body’s immune system or targeting specific genetic mutations within cancer cells to prevent their growth and spread.
Chemotherapy
Lastly, chemotherapy is another treatment option for melanoma. However, it is less commonly used than in the past. It involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. Chemotherapy may be used in cases where the melanoma has spread to other organs or when other treatments have not been effective.
Prevention Measures
Other methods can also help patients to manage their skin from the risk of melanoma. For instance, use sunscreen with the appropriate SPF for protection. Doing so will help prevent ultraviolet light from harming your skin and the development of melanoma in different areas of the body.
Meanwhile, another prevention step for fighting melanoma is regular skin self-examinations. By checking your skin regularly, you can detect any new moles or changes in existing ones. Thus, allowing individuals to address melanoma early on and receive effective treatment.
Moreover, seeking professional dermatological examinations at least once a year is crucial for the early detection of any suspicious skin lesions that may indicate melanoma. Early detection significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and recovery from this potentially life-threatening condition.
Conclusion
Understanding melanoma is essential for early detection, proper diagnosis, and effective treatment. By recognizing the symptoms, being aware of risk factors, and adopting preventative measures, individuals can take control of their skin health.
If you suspect any unusual changes or have concerns about your skin, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate guidance. Book an online consultation with a dermatologist today!
Melanoma Awareness Quiz
Test your knowledge about melanoma skin cancer