Knowing the significance of expressing emotions without the retaliation and judgment from others is an ideal world for mental health patients. Unfortunately, dealing with such expressions is not handled well by most people. Thus, resulting in several misunderstood scenarios. That’s why it is important to pursue and introduce mental health awareness in the community for a better handling and management of feelings without compromising relationships.
In this blog, we’ll discuss the stigma about mental health conditions, and spread understanding to create a more supportive and empathetic society. Let’s begin!
Understanding Mental Health

When we talk about mental health, we are not just referring to the overall state of a person’s mental well-being. Mental health is a complex and multifaceted aspect of human well-being. It goes beyond the absence of mental illness and encompasses a person’s emotional, psychological, and social well-being. In short, it is about having the ability to cope with the normal stresses of life, form and maintain meaningful relationships, and contribute to society in a positive way.
If someone has good mental health, they are able to think clearly, manage their emotions effectively, and navigate the challenges that life throws at them. On the other hand, poor mental health can lead to difficulties in coping with daily stressors, impaired decision-making, and strained relationships. Thus, showing the importance of raising awareness about mental health care for everyone.
The Importance of Mental Health in Everyday Life
Mental health plays a vital role in every aspect of our lives. It affects our ability to cope with stress, maintain healthy relationships. At the same time, it can influence our drive to achieve personal and professional goals. When we prioritize mental health, we can enhance our resilience, improve problem-solving skills, and experience a greater sense of happiness and fulfillment.
Furthermore, promoting mental health in society benefits everyone. When individuals are mentally healthy, they are more productive, engaged, and satisfied with their lives. This, in turn, leads to stronger communities and a more prosperous society as a whole.
On the other hand, when we neglect our mental health, it can have detrimental effects on our overall well-being. Unaddressed mental health issues can lead to increased risk of developing mental disorders, such as anxiety and depression. It can also impact our physical health, as the mind and body are interconnected.
By taking proactive steps to maintain good mental health, we can improve our overall quality of life. Engaging in self-care activities, seeking support from loved ones, and practicing stress management techniques are all essential in nurturing our mental well-being.
The Stigma Surrounding Mental Health

The stigma surrounding mental health is a complex issue that has deep historical roots. Throughout history, individuals with mental health conditions have often been marginalized, subjected to discrimination, and treated as outcasts. This stigma is perpetuated by societal beliefs, inadequate education, and negative media portrayals.
One of the origins of mental health stigma can be traced back to civilizations where it is often attributed to supernatural causes. This belief system led to the isolation and mistreatment of individuals with mental health conditions, as they were seen as dangerous or cursed. In short, it led to widespread persecution.
As society progressed, new theories emerged to explain mental health conditions. For instance, they discovered the connection of mental illness and moral weakness or personal failings. This perspective led to the stigmatization of individuals with mental health conditions, as they were viewed as lacking self-control or discipline.
The impact of stigma on individuals and society is profound. It prevents many individuals from seeking help, often due to fear of judgment or discrimination. Individuals facing mental health challenges often experience self-isolation and a sense of shame. They may feel compelled to hide their struggles, leading to a lack of social support and exacerbation of their symptoms. This can further perpetuate the cycle of stigma, as individuals may internalize negative beliefs about mental health and feel unworthy of help or understanding.
Common Mental Health Disorder
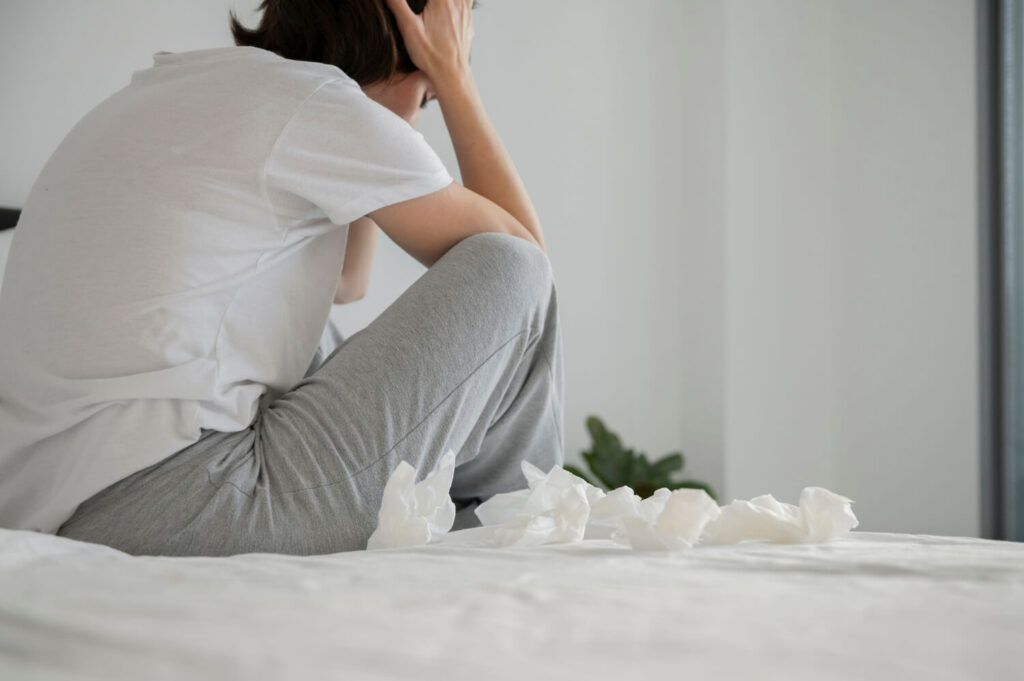

There are several mental health problems that people often disregard. With the constant struggle in the emotional health aspect, it is highly important to understand the disorders to manage them better in the future.
Here are the common mental health conditions:
Depression
This common health disorder is known for loss of interest and overall negative feelings about oneself. There’s also a constant feeling of sadness and pleasure to do things that individuals normally do in their daily life. Patients with this condition may also feel alone most of the time, which leads to affected relationships, especially among family members.
Anxiety
Furthermore, another condition that needs to be understood more is anxiety. Individuals with this condition may feel worried and fear at the same time. Thus leading to often panic attacks or anxiety attacks.
Schizophrenia
On the other hand, this condition warps the reality of the individual. Patients with schizophrenia often experience severe hallucinations that affect their understanding of reality. It is known for its extremity as it can disable people.
Bipolar Disorder
Meanwhile, individuals that often change mood, energy, and have lesser concentration abilities,.there’s a possibility they have bipolar disorder. Patients often don’t know they have this condition, which can affect their relationship with other people. With that, this mental health crisis is mostly known as manic depression.
Dissociative Identity Disorder
This disorder is known for having two or more personalities that often take control. In the psychology field, it is understood that the individual develops such personalities to protect oneself from reliving a bad memory. In short, dissociative identity disorder happens when there’s a traumatic experience that patients don’t want to deal with and escape by aiming to be another persona.
These various disorders are challenging to face, especially on your own. That’s why mental health promotion can make a huge difference as it can help educate more people about them. With mental health awareness, patients can find a strong support system that believes and can help as they go through the hoops of life. Thus, making mental healing possible by breaking down boundaries made by the ongoing stigma.
Strategies to Break Public Stigma
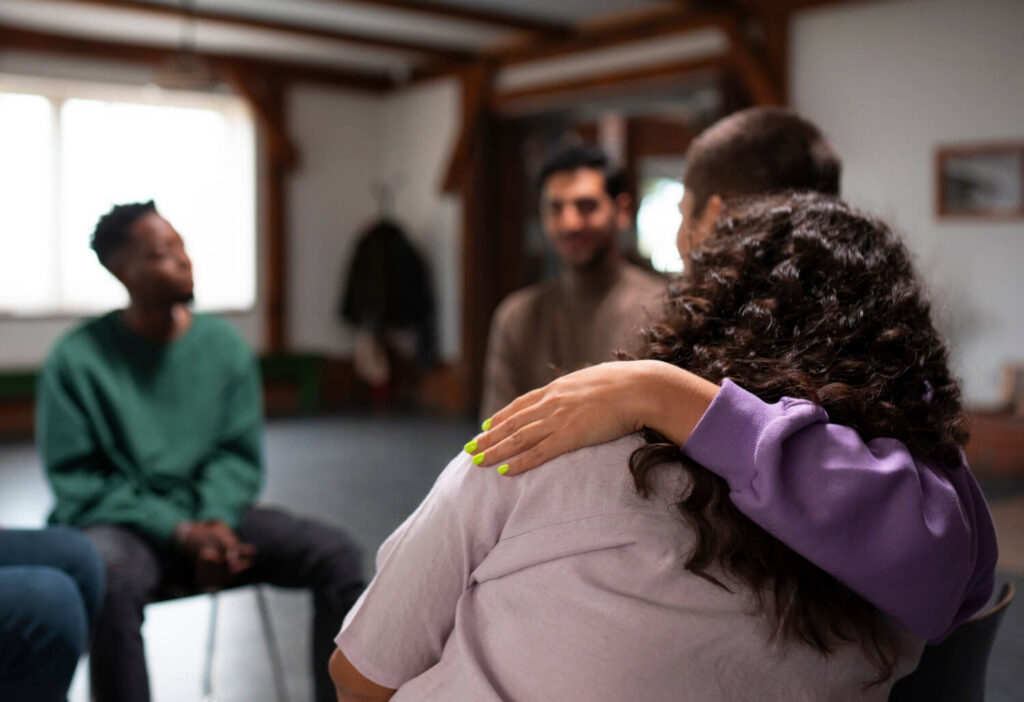

Education as a Tool for Change
A crucial step in combating mental health stigma is through education. By promoting accurate information about mental health and debunking common myths, we can help individuals develop a better understanding of mental illness.
At the same time, education plays a vital role in breaking the stigma surrounding mental health. When individuals are equipped with accurate knowledge about mental illness, they are more likely to recognize the signs and symptoms and seek appropriate help. By educating the public about the prevalence and diversity of mental health conditions, we can dispel misconceptions and foster a more inclusive society.
Furthermore, education helps individuals develop empathy and compassion towards those experiencing mental health challenges. By learning about the complexities of mental illness, individuals can better understand the struggles faced by those living with these conditions. This understanding can lead to a more supportive and inclusive environment, where individuals are less likely to judge or stigmatize others based on their mental health.
The Role of Media in Shaping Perceptions
The media has a significant influence on public perceptions and attitudes towards mental health. Responsible media coverage can help break down stereotypes and present mental health issues in a compassionate and informed manner. By highlighting stories of recovery, resilience, and successful treatment, media outlets can challenge stigma and inspire positive change.
However, it is important for the media to exercise caution and responsibility when reporting on mental health. Sensationalized or stigmatizing portrayals can perpetuate harmful stereotypes and reinforce negative attitudes. By adhering to ethical guidelines and consulting mental healthcare experts, media professionals can ensure that their coverage is accurate, balanced, and respectful.
Moreover, the media can play a crucial role in raising awareness and proactive approach about mental health. For instance informing the masses about the available resources and support services for individuals with mental health conditions. By providing information on helplines, support groups, and mental health treatment options, media outlets can connect individuals to the help they need and encourage them to seek assistance.
Mental Health Advocacy: Mental Health Awareness Month

Mental health advocacy serves as a powerful tool in raising awareness and driving societal change. Through grassroots movements, community engagement, and lobbying efforts, advocates can influence policies, funding, and public attitudes towards mental health. By amplifying the voices of those with lived experiences, mental health advocates strive for a more inclusive and supportive society.
Advocacy is not limited to a specific group or organization; it is a collective effort that requires the participation of individuals, communities, and policymakers. Mental health advocates play a crucial role in challenging stigmas, promoting education, and advocating for accessible and affordable mental health services.
For instance, celebrating various advocacies such as embracing the mental health awareness month. This powerful tool can help in raising mental health awareness and driving societal change. Furthermore, this important social movement can encourage other people to join and learn more about mental fitness and the risks that can affect it. Thus, making people understand more and break the cycle of stigma.
Implementing Mental Health Programs in Communities
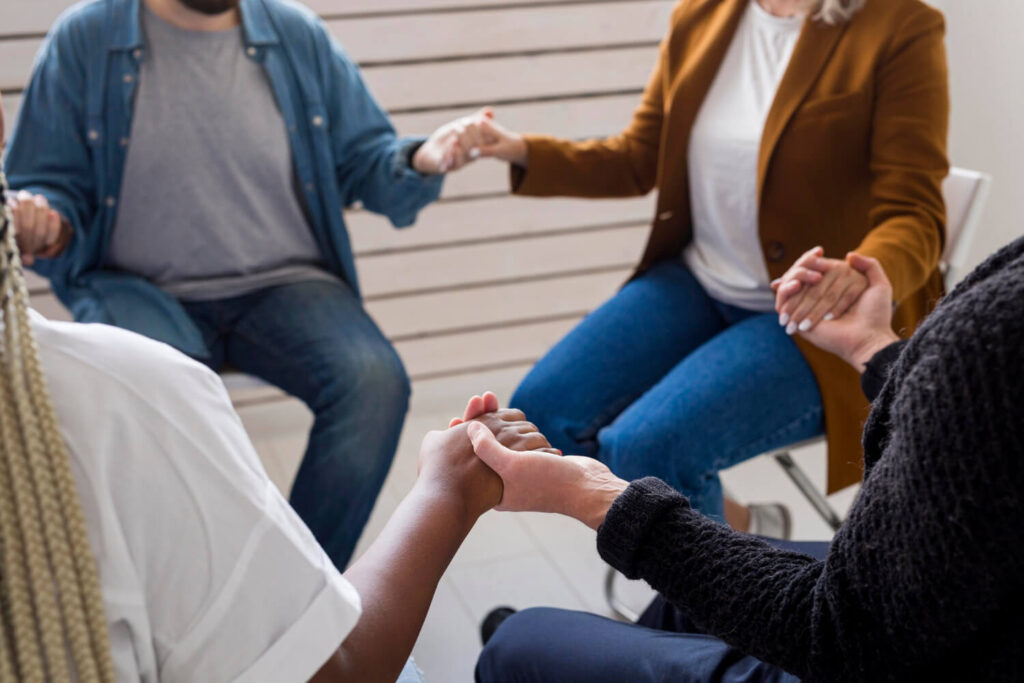

Tangible action is vital in promoting mental health awareness. Communities must establish and support mental health programs that provide individuals with necessary resources, support networks, and access to affordable and quality care. By integrating mental health into schools, workplaces, and community centers, we can ensure that no one is left behind or feels alone in their struggles.
Here’s how integrating programs in various forms of community can help:
School
Implementing mental health programs in schools is crucial for early intervention and prevention. By incorporating mental health education into the curriculum, students can develop a better understanding of mental health, learn coping mechanisms, and feel empowered to seek help when needed. Additionally, schools can provide counseling services and create safe spaces where students can openly discuss their mental health concerns without fear of judgment or stigma.
Workplace
Meanwhile, workplaces also play a significant role in promoting mental health. Employers can implement policies that prioritize employee well-being, such as flexible work arrangements, mental health days, and access to counseling services. By fostering a supportive work environment, employers can contribute to the overall mental well-being of their employees and reduce stress-related issues.
Community Center
Lastly, having a supportive community should have community centers that can serve as vital hubs for mental health support. By creating a sense of community and providing a safe space for individuals to connect and share their experiences, community centers can play a crucial role in destigmatizing mental health and fostering a supportive environment.
Final Takeaway
As we strive to create a more inclusive and understanding society, promoting mental health awareness and breaking stigma is vital. By educating ourselves and others, challenging misconceptions, and advocating for change, we can create a world where individuals facing mental health challenges receive the support and compassion they deserve. Together, we have the power to break the silence and build a brighter future for mental health.If you are currently suffering from a mental health condition and need help, don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment with a healthcare professional. Book an online consultation or visit a psychiatrist today!
Mental Health Awareness Quiz
Test your knowledge about mental health and well-being