Pregnancy is a crucial condition that should be closely monitored. During this stage, the mother is at risk for several possible illnesses due to physical changes. One of the vital aspect involves the risk of high blood pressure. That’s why monitoring normal bp in pregnancy is a must to ensure maternal health.
Explore our comprehensive overview and understand the importance of monitoring pregnancy term. Let’s begin!
Understanding Blood Pressure: A Brief Overview
Blood pressure is a measure of the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps it through the body. It consists of two values: systolic pressure, which is the pressure when the heart contracts, and diastolic pressure, which is the pressure when the heart relaxes between beats.
The blood pressure is expressed in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is commonly written as systolic/diastolic. This measurement is used by health experts to ensure normal bp in pregnancy. For instance, blood pressure 110/70 has a 110 systolic and 70 diastolic.
Role of Blood Pressure in Pregnancy
Blood pressure is an important indicator of cardiovascular health. It ensures that oxygen and nutrient-rich blood reaches all the organs and tissues in the body, including the placenta during pregnancy. Maintaining normal bp in pregnancy is vital for the proper functioning of the circulatory system of mothers and the baby.
When blood pressure is too high, it can strain the arteries and lead to serious health conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. On the other hand, low blood pressure can cause dizziness, fainting, and inadequate blood flow to the organs. Therefore, understanding and managing blood pressure is crucial for maintaining overall well-being.
Several factors can influence blood pressure. If it falls outside the normal range, seek medical advise immediately.
How is Blood Pressure Measured?
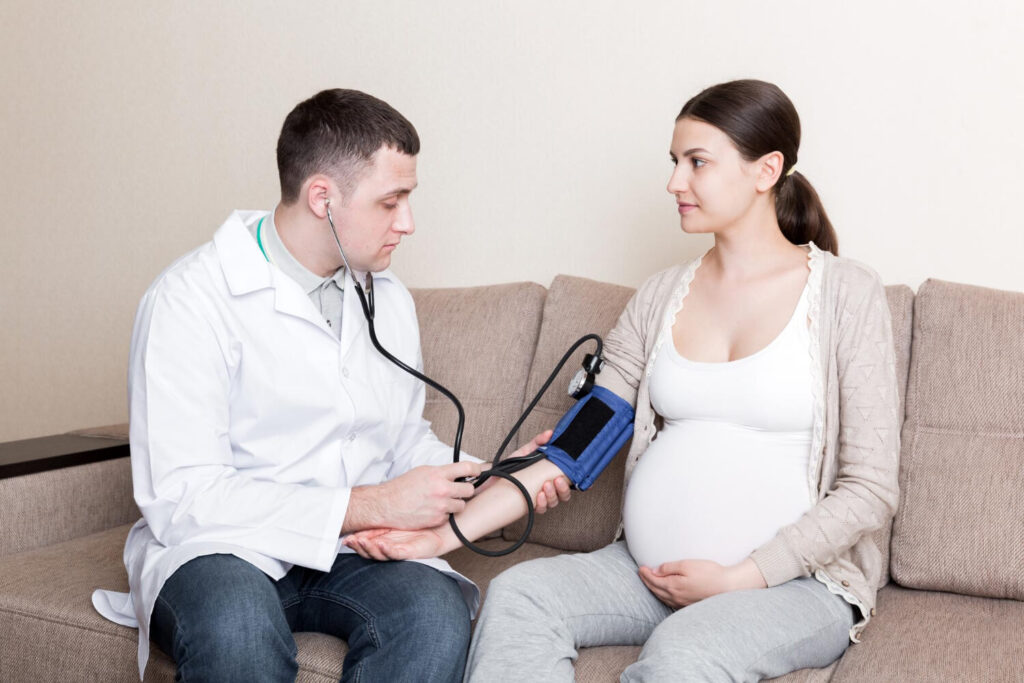

Blood pressure is typically measured using a device called a sphygmomanometer. It consists of an inflatable cuff that goes around the upper arm and a pressure gauge. The cuff is inflated and slowly deflated while the healthcare professional listens for blood flow sounds using a stethoscope. The two values, systolic and diastolic, are recorded.
Understanding blood pressure measurement and the factors that can influence it is crucial for individuals to take proactive steps in managing their cardiovascular health. Regular monitoring, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and following medical advice can help maintain optimal blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of associated complications.
The Importance of Monitoring Blood Pressure During Pregnancy
Monitoring blood pressure during pregnancy is crucial for both the mother’s and baby’s health. High blood pressure can lead to complications like organ damage, while low blood pressure may cause dizziness and fainting. Regular blood pressure monitoring allows healthcare providers to detect any abnormalities early and take appropriate actions.
Pregnancy is a time of significant physiological changes in a woman’s body. The cardiovascular system undergoes adaptations to support the growing fetus and maintain adequate blood flow to the placenta. These changes can affect blood pressure levels, making monitoring essential to check if normal bp in pregnancy is achieved.
Risks Associated with High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure during pregnancy, especially if left untreated, can lead to serious complications. It may increase the risk of preterm birth, slow fetal growth, placental problems, and even preeclampsia. Preeclampsia is a condition characterized by high blood pressure and organ damage. This condition is mostly a threat to the liver and kidneys, which can affect both the mother and the baby.
Regular blood pressure monitoring enables healthcare providers to closely monitor any elevation in blood pressure and take appropriate measures to manage it. This may include lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and increased physical activity, or medication if necessary. By addressing high blood pressure early on, the risks associated with it can be minimized, promoting a healthier pregnancy outcome.
Risks Associated with Low Blood Pressure
While low blood pressure during pregnancy is less common, it can still pose risks. Symptoms may include dizziness, fainting, and reduced blood flow to the placenta, affecting the baby’s growth. Low blood pressure can be caused by factors such as hormonal changes, dehydration, or certain medical conditions.
Monitoring blood pressure helps identify low levels and prevent potential complications. Healthcare providers can assess the severity of low blood pressure and provide appropriate interventions. These may include increasing fluid intake, adjusting dietary habits, or recommending specific exercises to improve blood circulation.
It is important to note that blood pressure can fluctuate during pregnancy due to various factors, such as stress, physical activity, and hormonal changes. Regular monitoring allows healthcare providers to track these fluctuations and identify any patterns or abnormalities that may require further evaluation.
What is Normal BP in Pregnancy?

Blood pressure can vary throughout pregnancy. Here’s what to expect during each trimester:
First Trimester: What to Expect
During the first trimester, blood pressure may drop slightly due to hormonal changes and expansion of blood vessels. It is generally lower than pre-pregnancy levels, but still within normal ranges.
As the body adjusts to the changes of pregnancy, the blood vessels relax and widen. This allows for increased blood flow to the developing fetus and placenta. The hormonal changes also play a role in lowering blood pressure during this trimester.
It is important to note that while a slight decrease with the normal bp in pregnancy is normal, any significant drop should be discussed with your healthcare provider. They will be able to evaluate your individual situation and provide appropriate guidance.
Second Trimester: What to Expect
Blood pressure starts to increase during the second trimester but usually remains within a healthy range. It tends to stabilize or even decrease slightly during this period.
During the second trimester, the body continues to adapt to the growing fetus and the demands of pregnancy. The blood volume increases, and the heart works harder to pump blood throughout the body. These changes can lead to a slight increase in blood pressure.
However, it is important to note that a significant rise in blood pressure during the second trimester may indicate the development of gestational hypertension or preeclampsia. Regular monitoring and communication with your healthcare provider are crucial to ensure the well-being of both you and your baby.
Third Trimester: What to Expect
Blood pressure gradually increases during the third trimester but should not exceed the upper limits of the normal range. Regular monitoring becomes even more important during this stage to detect any signs of gestational hypertension or preeclampsia.
As the pregnancy progresses into the third trimester, blood pressure tends to rise gradually. This is due to the increased workload on the cardiovascular system as the baby grows and the demands on the body intensify.
Regular prenatal check-ups are crucial during the third trimester to monitor blood pressure and detect any signs of complications. Gestational hypertension and preeclampsia are serious conditions that can develop during this time, and early detection is key for appropriate management and the well-being of both mother and baby.
It is important to remember that every pregnancy is unique, and blood pressure can vary from woman to woman. Your healthcare provider will closely monitor your blood pressure throughout your pregnancy and provide personalized guidance based on your individual circumstances.
Conditions Affecting Blood Pressure During Pregnancy

When normal bp in pregnancy is not met, there are there are several conditions that patients must take note of. It is important to be aware of these conditions and seek appropriate medical care if needed. Let’s take a closer look at each of them:
Gestational Hypertension
Gestational hypertension is a condition in which a woman develops high blood pressure after the 20th week of pregnancy. Unlike chronic hypertension, which is present before pregnancy, gestational hypertension typically resolves after childbirth. However, it still requires close monitoring to prevent complications.
When a woman has gestational hypertension, her blood pressure may rise above the normal range of 120/80 mmHg. This increase in blood pressure can put extra strain on the heart and blood vessels, potentially leading to complications such as preeclampsia.
In order to manage gestational hypertension, healthcare providers may recommend regular blood pressure monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes medication. It is crucial for pregnant women with this condition to attend all prenatal appointments and follow their healthcare provider’s guidance closely.
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy and is characterized by high blood pressure and organ damage, typically affecting the liver and kidneys. It is one of the leading causes of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality worldwide.
Women with preeclampsia may experience symptoms such as severe headaches, vision changes, swelling in the hands and face, and abdominal pain. If left untreated, preeclampsia can lead to complications such as placental abruption, fetal growth restriction, and even eclampsia, which is a life-threatening condition characterized by seizures.
Managing preeclampsia involves close monitoring of blood pressure, regular prenatal check-ups, and sometimes hospitalization for more severe cases. Healthcare providers may also recommend bed rest, dietary changes, and medications to help control blood pressure and prevent further damage to organs.
Chronic Hypertension
Chronic hypertension refers to high blood pressure that is present before pregnancy or is discovered before the 20th week of gestation. Women with chronic hypertension require careful management and monitoring throughout pregnancy to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
When a woman has chronic hypertension, her blood pressure is consistently elevated, exceeding the normal range. This can increase the risk of complications such as preeclampsia, preterm birth, and growth restriction in the baby.
Healthcare providers will closely monitor blood pressure levels and may adjust medication or recommend lifestyle modifications to help maintain blood pressure within a safe range. Regular prenatal visits, including ultrasounds, will also be scheduled to assess the baby’s growth and well-being.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Blood Pressure During Pregnancy
While blood pressure can fluctuate during pregnancy, there are steps you can take to help maintain healthy levels:
Diet and Nutrition
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products can help support overall cardiovascular health. Limiting salt intake and avoiding processed foods can also contribute to maintaining healthy blood pressure.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga, can help regulate blood pressure. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting or modifying any exercise routine during pregnancy.
Final Takeaway
Monitoring maternal health during pregnancy is of utmost importance. Ensuring normal bp in pregnancy occurs is a huge deal for it prevents risks for both the mother and the child. Furthermore, it secures the overall journey of the mother during the physical changes that happen.
If fluctuation in blood pressure occurs during pregnancy, it is a serious situation that needs medical assistance. Make sure to consult with the health care expert to monitor the condition.